Use the Import Data feature to add new items or update existing items from a spreadsheet. You can import items into an auxiliary table or a specific project in a primary table (application table).
Preparing a Spreadsheet for Importing Data
The key to achieving a successful import lies in taking the time to prepare source data for importing. This requires an intimate knowledge of the field types and existing data in your system, and of the data you are importing.
Spreadsheets used to import data must adhere to the following requirements:
- Only files of type .xls can be imported. If you have an .xlsx file or any other type of spreadsheet file, you must convert it to .xls.
- Only data from the first worksheet in a file is imported.
- You can only import one spreadsheet at a time.
- You can only import into a single project or auxiliary table at a time.
- Spreadsheet columns represent SBM fields and all spreadsheet data is treated as text. Spreadsheet columns must be formatted as Text types.
- Each row represents an item that will be imported, except for the first row, which is used to define columns available for mapping. Data from this row is never imported.
- To import primary items, the spreadsheet must include columns for the system State and Title fields.
- To import auxiliary items, the spreadsheet must include a column for the system Title field.
- If you are using the import to update items, include a column that can be used to determine uniqueness. For details, refer to Record Matching.
- For best results, limit the number of rows to 10,000. To import more than 10,000 items, create multiple spreadsheets and import them separately.
- To ease data mapping, label spreadsheet columns with the same name as your SBM fields. This enables you to use auto mapping.
- Ensure that all spreadsheet fields are in the "Print Area". If they are not in the print area, they will not be available for data mapping.
- Also, ensure that none of the rows or columns are selected under "Freeze Panes".
Here is an example of a simple spreadsheet used to import users:
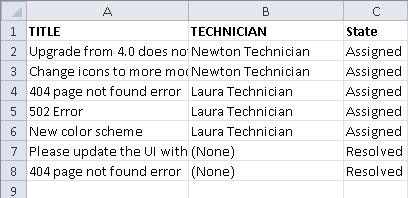
In this example, row 1 defines the columns to be mapped. This information is not imported. Row 2 is used as sample data, but data is imported.
Import Privileges
The following privileges are required before administrators can import new items or update existing items.
| Privilege | Privilege Location | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Remote Administration | User - System page | Grant to enable administrators to log into SBM Application Administrator. |
| Submit New Items | User - Item page (primary items)
User - Table page (auxiliary items) |
Grant to enable administrators to import new items to a specific project or auxiliary table. |
| Update All Items | User - Item page (primary items)
User - Table page (auxiliary items) |
Grant to enable administrators to use the Data Import feature to update existing items. |
Record Matching
To use the Import Data feature to update existing primary and auxiliary items in your system, you need a field in your application that contains a unique value for each primary and auxiliary item and a column in the spreadsheet that contains unique values for each row. You must then map the unique SBM field to the spreadsheet column that contains unique values.
During the import process, the value of each row is matched against existing values in the system. Matching is case insensitive.
Field Mapping Considerations
You can map to most SBM fields; exceptions are the Project field, Folder fields, Sub-Relational fields, the system-provided Last Incident field, and deleted fields.
The following information provides guidance on mapping to specific fields or field types.
Item IDs
- To automatically generate Item IDs for newly imported items, do not map a spreadsheet column to the Item ID field. When IDs are generated, numbering properties specified for the project apply to the imported items.
- To retain Item IDs from data in the spreadsheet, map the ID column to the Item ID field, but be aware that doing so overrides the system's automatic ID generation and may result in duplicate Item IDs.
- To retain historical data while automatically generating Item IDs, consider creating a custom field to store imported IDs and mapping to this field when you import data. For example, in SBM Composer, create a Text field named Old ID Numbers. After deployment, you can map the ID column in the spreadsheet to the Old ID Numbers field. This enables users to search for the old ID numbers, but ensures unique, system-generated IDs in imported items.
- If you use Item Type prefixes, such as ENH for enhancements, include a column in the spreadsheet for item types (Requests, for example) and map this column to the system Item Type field. Each spreadsheet row can contain either the Item Type value, such as Request, or a prefix, such as REQ. SBM will match spreadsheet values to Item Type prefixes and values specified in SBM Composer.
- When you import primary items, you must map a spreadsheet column to the State field.
- Each row in a column mapped to the State field must have valid data. Rows that do not have a State field value are skipped. If a row contains a value that does not match an existing state, the row is skipped.
- SBM states use the Active/Inactive field to automatically determine the status of items in each state. You can map to the Active/Inactive field, but it is more beneficial to use the automatic setting of the Active/Inactive field.
- After importing data, review imported items to ensure they are owned by the correct users.
Selection Values
- Single Selection
- Multi-Selection
- User
- Multi-User
- Single Relational
- Multi-Relational
- Multi-Group
Data in spreadsheet rows for columns mapped to selection fields must match existing data in the system. If not, the row is skipped. Matching is based on case-insensitive searches of the selections available for a field. For User fields, matching is based on the login ID or name of users in the system.
Users can be specified by their names or login IDs. You can use the Parse multiple values in a cell option to specify a separator, and then import several values within one spreadsheet cell.
Use the Replace data in Multi- type fields option if you want to overwrite Multi-User, Multi-Group, Multi-Selection, and Multi-Relational fields instead of adding new selections to those field types.
For fields that allow you to select users and groups, you do not need to specify which name is in a cell (either the user or the group)—the import attempts to determine this automatically. The import process attempts to find a user with the specified name or login ID. If it is not found, then it attempts to find a group with that name. This means that if you have a user and a group with the same name and you specify this name in the spreadsheet, the user name is set as the field value.
Empty rows are imported as "none" values unless you select the Set default values for empty cells check box and the mapped field has a default value.
- Spreadsheet columns must be formatted as Text types, including
those for
Date/Time fields. For best results, row data for
Date/Time fields should follow these guidelines:
- For SBM fields that are set as Date Only or Date and Time, spreadsheet data should match the display format, such as mm/dd/yyyy or mm/dd/yyyy hh:mm:ss. After the import process, values will appear to users in the format specified in their user profile.
- In addition, ensure that the format of the values in the spreadsheet matches the Date Format that is selected in your user profile.
- Date/Time keywords, such as startof_lastweek or endof_thisyear, can be used with Date/Time fields set as Date Only or Date and Time.
- For Time Only or Elapsed Time fields, specify spreadsheet values in this format: hh:mm, hh:mm:ss, or d hh:mm:ss (Elapsed Time fields only).
- If you do not map to system Date/Time fields, such as Submit Date and Close Date, values may be established as the date items were imported.
Text Field Values
Spreadsheet data should comply with Text field settings. For example, if you map to a Text field set to have a fixed length of 80 characters and a spreadsheet row has 100 characters, the last 20 characters are truncated in the imported item.