The SSM solutions contain the following process apps:
| Solution | Process Apps |
|---|---|
| Service Support Manager |
Incident Management focuses on restoring normal service operations as quickly as possible to minimize the impact of incidents on business operations, thus ensuring that the best possible levels of service quality and availability are maintained. Problem Management analyzes the root cause of incidents, prevents their recurrence, and limits the impact of problems that cannot be prevented. Problem management includes the Workarounds auxiliary table, where information about workarounds is stored. Change Management helps ensure that standardized methods and procedures are used for efficient and prompt handling of all changes to controlled IT infrastructure. This minimizes the number and impact of any related incidents upon service after changes are implemented. Configuration Management System (CMS) oversees the life of Configuration Items (CIs) by enabling the fundamental elements of identification, change management, status accounting, and audits. CMS components include the Configuration Items table, where all CIs and CI baselines are stored, the "BaselineWorkflows" orchestration where CI baselines are processed, and the Relationships auxiliary table where the relationships between CIs, RFCs, Problems, and Incidents are stored. Asset Management helps you monitor requests for assets, track business and financial approvals, and calculate depreciation values for each asset. You can easily report on assets in your inventory, incoming asset requests, and assets assigned to individual employees. You can also quickly see year-to-date depreciation numbers, along with depreciation of assets by department. |
| Service Request Center |
Service Request addresses requests from users by providing a request channel, gathering or supplying information, and fulfilling the request. Knowledge Management manages knowledge base articles and announcements. It provides the ability to submit new knowledge base articles, specify whether articles are public or private, and monitor changes to existing articles. Starter Pack Forms - IT provide pre-built forms for commonly used IT services, such as password change requests and software installs. |
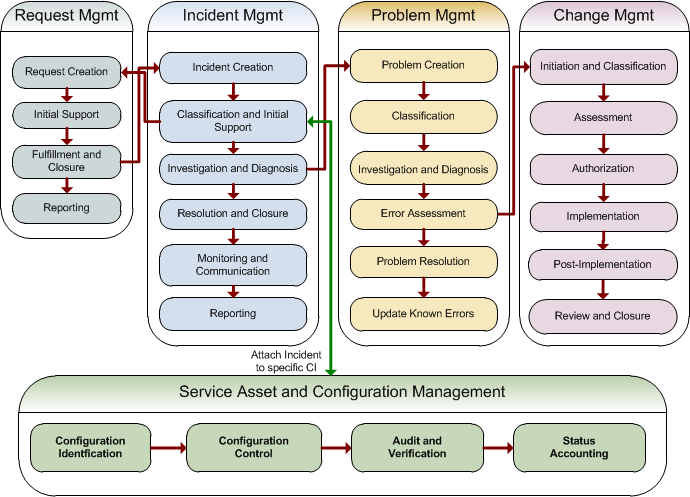
The following illustration shows the SSM and SRC process components and how they work together:
- Configuration items (CIs) are entered and stored in the Configuration Management System.
- Users or IT Service Desk staff submit a request, which can lead to the creation of an incident.
- After the incident is assigned, a CI can be selected, which creates a link between the incident and the CI.
- If the incident needs to be escalated for root cause analysis, a problem can be submitted based on the incident.
- Problems can lead to entries in the Workarounds table that document workarounds for problems, and resolutions to known errors.
- A Request for Change (RFC), which is a formal proposal for a change to the IT infrastructure, may be required.
- An RFC may require an update to a CI and a new CI baseline.
The following topics describe the SSM process apps in detail.