The Deployment Automation server provides a variety of services, such as:
- the user interface
- component and application configuration tools
- workflow engine
- security services
A service can be thought of as a self-contained mechanism for hosting a piece of business logic. Services can be consumed by clients, agents, or other services.
Many Deployment Automation services are REST-type (representational state transfer). REST-type services are web services that focus on transferring resources over HTTP.
Workflow requests are initiated with either the web application user interface or the CLI (command line interface). When a workflow is requested, many services are used to fulfill the request.
Figure 1. Services and Process Workflow
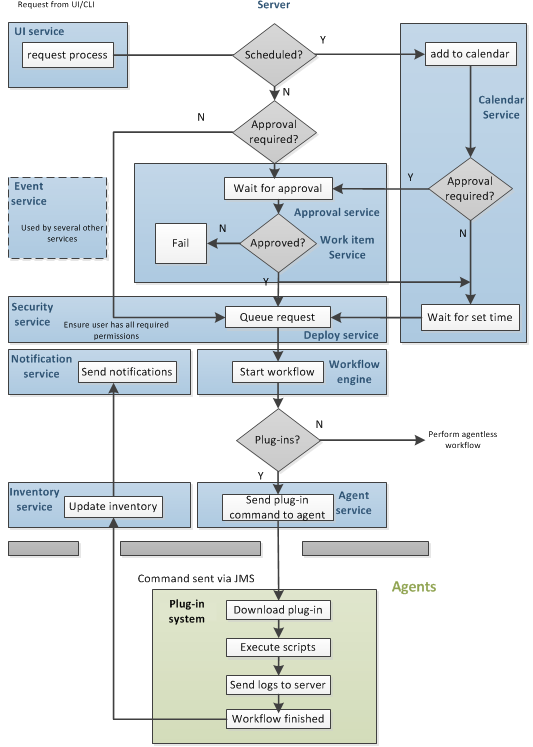
| Service | Description |
|---|---|
| User Interface | Used to create components and fashion workflows, request processes and manage security and resources, among other things. REST-based. |
| Workflow Engine | Manages workflows, application and component processes. Calls the agent responsible for performing the workflow's current plug-in step. When the workflow is finished, alerts the notification and inventory services. Called by the deploy service. REST-based. |
| Agent | Tracks installed agents and routes plug-in commands to affected agents. Commands come from plug-in steps. Invoked by the workflow service. REST-based. |
| Work Item | Operates in tandem with the approval service; provides approver alerts and enables approvers to accept or reject workflows. If a scheduled workflow remains unapproved at run-time, the job fails automatically. REST-based. |
| Plug-in Manager | Deployment Automation
can interact with virtually any system through its extensible plug-in system;
plug-ins provide functions by breaking-down tool features into automated steps.
Plug-ins can be configured at design- and run-time. When a plug-in step
executes, the controlling agent invokes its run-time process to execute the
step.
When a new component version is available, the agent compares the current component version and downloads and only new or changed artifacts. |
| Event | The event service is ubiquitous; it alerts other services as various trigger conditions occur. |
| Deployment Service | Manages deployments. When a deployment process is requested, invokes the workflow engine to perform the process. Works in tandem with the security service to ensure users have required permissions. REST-based. |
| Notification Manager | Notifies users about the status of deployments; notifications are sent to approvers if the system is configured with an e-mail server and the user has an e-mail address. Invoked by the workflow manager. REST-based. |
| Inventory Manager | When a workflow finishes, the inventory manager updates affected inventory records. Deployment Automation maintains an inventory of every deployed artifact in every environment, which provides complete visibility across environments. REST-type service. |
| Approval Engine | Enables creation of approval-requiring jobs and approver roles. Works in tandem with the work item service to ensure required approvals are made before scheduled jobs. REST-based. |
| Security | Controls what users can do and see; maps to organizational structures by teams, roles, activities, etc. REST-based. |
| Calendar | Used to schedule processes to being at some future point; works in tandem with the approval and work item services. REST-based. |
| CodeStation | Handles versioning of artifacts; agents invoke it when downloading component versions. REST-based. |