Getting Started
What is Dimensions CM Pulse?
Dimensions CM Pulse is a tool for developers that enables you to:
- Plan your team's work using requests. A request is a single unit of work, equivalent to a story in Agile, that can report a defect, suggest an enhancement, or detail other work for a particular product.
- Organize your team’s work in backlogs. A backlog enables you to plan your team’s work and group requests into common areas using a prioritized hierarchy of epics and features.
- Execute requests in iterations. An iteration is one development cycle, commonly known as a sprint, which is typically a few weeks. An iteration includes the requests your team are confident they can complete during the sprint.
- Review the health and quality of changes to help you determine if they are ready to be merged or released.
- Use experts to inspect your source code and report back findings.
- Collaborate with team members to conduct peer reviews of code changes.
- Comment on reviews and collaborate with peers to improve the quality of code.
- View recent activity in your streams.
- Visualize changes in your streams, branches, and merges on the changeset graph.
- Run reports to display statistics and trends in your streams.
Videos
Click a link like this Video: CM 14 Overview to watch videos of Dimensions CM features in the Serena Documentation Center.
Quick Tour
Watch a quick tour to learn more about Pulse.
Navigate
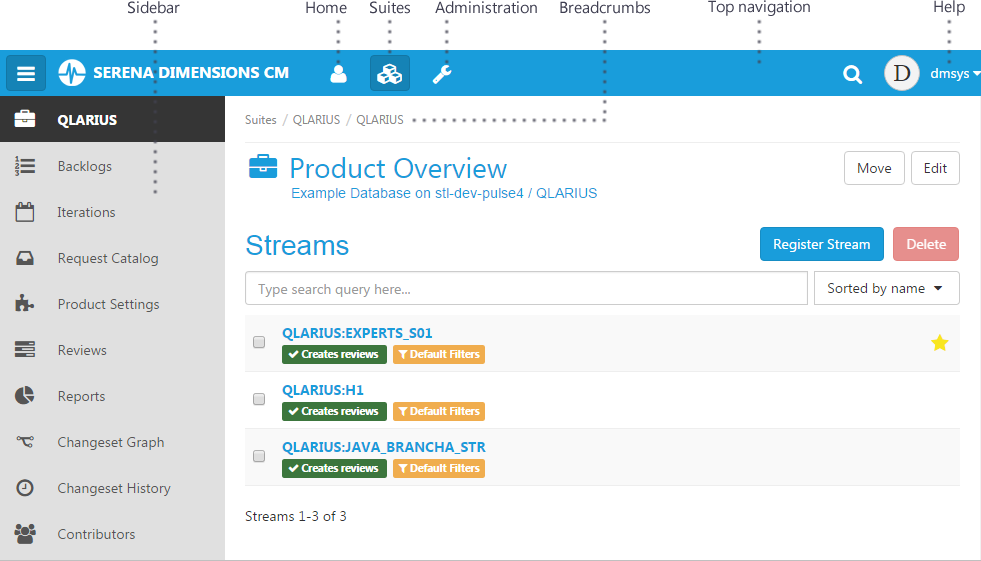
Top Navigation
The top navigation contains:
- Links to Home, Suites, and Administration.
- A search field.
- A drop-down menu with links to the quick tour, help, and Serena Central.
Sidebar
The sidebar contains links that are relevant to your current location in the Pulse hierarchy.
Breadcrumbs
Breadcrumbs display your current location in the Pulse hierarchy.
Home
The Home page displays useful information for the user who is currently logged into Pulse, including:
- Recent activity by the user such, as the results of expert chains for deliveries they have made, and reviews they have commented on.
- The number of reviews that require the user's attention.
- The number of reviews owned by the user.
- The number of requests in the user's Inbox.
- Streams that the user has recently delivered to.
- Backlogs and iterations the user has recently used.
The Home page sidebar has links to information related to the current user, such as a list of reviews, changeset history, email notifications, and user preferences.
To open the Home page for the current user, on the top navigation click Home.
Search
You can search Pulse for specific reviews. A search is scoped to where you are in the Pulse hierarchy, for example, a stream.
- To restrict the scope of the search, select a suite, product, stream, or Home (the current user).
- Click Search on the top navigation and enter a string that matches one of the following search types:
- A review's unique label, for example, Q234 (only complete matches are shown).
- A Dimensions CM request, for example, QLARIUS_CR_44 (only complete matches are shown). A Dimensions CM request can be related to one or more reviews.
- A user who owns reviews, for example, David (you can enter part of a name).
- A review's title, for example, Refactoring (you can enter part of the title).
NOTE Search is not case-sensitive. - Click Search or press Return. The results are displayed in the Search Results page. Click a result to view more details.
- To refine your search, do one of the following:
- Select a filter from one of the results lists. The filter appears in the Refined by box:
- Control-click to select multiple filters from the lists. In the Refined by box click Apply. The box is updated:
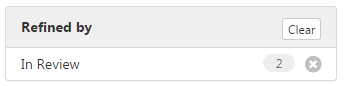
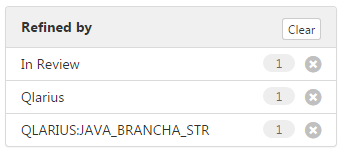
The Search Results window is updated. You can further refine your search by removing filters from the Refined by box.
Click Clear to remove all filters.
Keyboard Shortcuts
On Review and Changeset pages you can use these keyboard shortcuts:

Suites and Products
About Suites and Products
Administrators can organize work into suites and register CM products.
- A suite is a collection of related products, for example, Insurance. A suite can contain one or more Dimensions CM products, for example, Life Insurance and Health Insurance. You can register products in Pulse so that it will respond to events produced from those products.
- A product is the same as a Dimensions CM product and is a major unit of software development. A product is a collection of CM streams, for example, the product Life Insurance contains these streams:
- LIFE
- DISCOUNTS
- PROMOTION
- A stream is the same as a Dimensions CM stream or project and represents a branch or feature of development.
Use the following workflow to create a suite, add products, and configure streams:
- Create a suite.
- Register one or more products to the suite.
- Configure settings and defaults for each product.
- Optional:
- Register one or more streams with each product (streams are normally registered automatically).
- Configure the automatic creation of reviews and running of expert chains for each stream.
View Activity for Suites, Products, and Streams
When you select a suite, product, or stream its latest activity is displayed in the main window, including:
- New reviews that are created after deliveries to streams.
- New changesets that are delivered to streams.
- Changes to reviews' states.
- Comments on reviews.
- Expert chain results.
Activity is scoped to the suite, product, or stream where you are currently located.
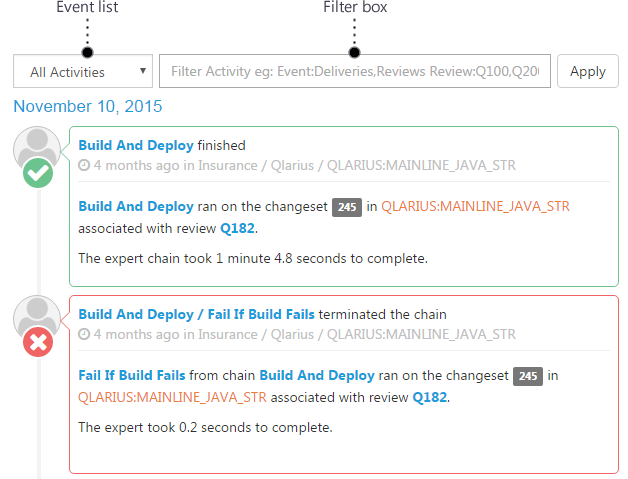
Filter the Activity Feed
To filter the information that is displayed in an activity feed, do one of the following:
- From the Activities list select an event type.
- In the Filter box enter a query in the format <filter name>:<value> and click Apply.
The filters names and values that you can specify are:
| Filter Name | Value | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Event | A comma-separated list of one or more of: Deliveries, Reviews, Votes, Comments, ExpertChains These correspond to the values in the Activities list. |
Event:Deliveries,Votes,ExpertChains |
| Review | A comma-separated list of one or more review labels. | Review:Q1,Q2,Q3 |
| Changeset | A comma-separated list of one or more changeset IDs. | Changeset:123,124,125 |
| Date | A date (in the format yyyy-mm-dd) or date range (in the format yyyy-mm-dd,yyyy-mm-dd) | Date:2016-10-01,2016-10-31 |
- To specify multiple filters in the same query, separate them with a space.
- To clear all filters, delete all the entries in the Filter box and click Apply.
- The Filter box is case-sensitive.
Examples:
- To display review Q900: Review:Q900
- To display the reviews Q900 and Q950: Review:Q900,Q950
- To display all activity on December 4th 2015: Date:2015-12-04
- To display all deliveries between December 4th and 10th 2015: Event:Deliveries Date:2015-11-4,2015-11-10
Create Suites and Register Products
Administrators can create new suites and register Dimensions CM products.
Create a New Suite
- On the top navigation click Suites.
- Click New Suite.
- Enter a title for the new suite.
- Optionally enter a description for the suite. Use the tools to format, and preview, the description.
- Click Save.
Register a Product to a Suite
- Select the suite where you want to register the product.
- Click Register and select Single Product.
- Enter a title for the product. A Pulse product is the same as a Dimensions CM product but the titles can be different.
- Optionally enter a description for the Pulse product. Use the tools to format, and preview, the description.
- From the Repository Name list do one of the following:
- Select an existing Dimensions CM repository.
- Select Create new repository.
- If you are creating a new repository do the following:
- Enter a title for the Dimensions CM repository.
- Enter the network address of the Dimensions CM server, for example:
dmcm-server.example.com - Enter the CM base database name and connection string, for example:
CM_TYPICAL@DIM14 - For SCM Credentials, select or deselect the option Always use the following credentials. Click here for information about using this option.
- Enter a Dimensions CM account username and password.
- From the Product in Repository list select a CM product.
- Click Register.
Register Multiple Products to a Suite
- Select the suite where you want to register the products.
- Click Register and select Multiple Products.
- From the Repository Name list do one of the following:
- Select an existing Dimensions CM repository.
- Select Create new repository.
- If you are creating a new repository do the following:
- Enter a title for the Dimensions CM repository.
- Enter the network address of the Dimensions CM server, for example:
dmcm-server.example.com - Enter the CM base database name and connection string, for example:
CM_TYPICAL@DIM14 - For SCM Credentials, select or deselect the option Always use the following credentials. Click here for information about using this option.
- Enter a Dimensions CM account username and password.
- From the Products in Repository list shift-click to select multiple CM products.
- Click Register. The new Pulse products have the same titles as the CM products. You can edit the titles later.
Configure Product Settings and Defaults
Set Default Review Check List and Rules
Administrators can set the default review check list and rules for a product.
You might want different products to show different check lists when users approve or reject reviews, and rules control how reviews move from one state to another (for example, whether all reviewers must approve a review, or just one).
- Select the product where you want to set defaults.
- On the sidebar select Product Settings.
- Select Review Defaults.
- From the Review Check List select one of the following:
- A review check list name
- Do not use a review check list by default
- From the Review Rules To Use list select a rule.
- Click Save.
Set Default Delivery Filter
Administrators can set the default delivery filter for a product and automatically assign it to any streams that do not have a filter. A product can only have one default delivery filter.
Delivery filters determine which changesets will create a review or run expert chains. For example, you could exclude deliveries of built artefacts made on behalf of your automated CI system in those products where CI was configured.
- Select the product where you want to set defaults.
- On the sidebar select Delivery Filters.
- Select a delivery filter and click Set As Default. If there is no delivery filter, create a new one.
- Click Make Delivery Filter Default.
Register a Stream to a Product
Streams are registered automatically in a Pulse product when anyone makes a delivery to that stream in Dimensions CM. However, administrators can manually register a stream, for example, to add an expert chain before the next delivery to that stream.
- Select the product where you want register a stream.
- Click Register Stream.
- In the Stream Name box start typing the name of a stream. Pulse automatically displays a list of all the streams that match the string (not case sensitive).
TIP Use wildcards to help you find a stream:
- Type '*' at the end of a string to match specific names, for example: DEV:STREAM_A*
- Type '*' to display all the streams in a Dimensions CM product.
- Select a stream.
- Click Save. The stream is registered with the product and you can now:
- Configure the stream to automatically create reviews and run expert chains.
- Add experts to expert chains.
Delete Suites, Products, and Streams
Administrators can delete suites and products and unregister streams.
- On the top navigation click Suites.
- Do one of the following:
- Select one or more suites.
- Select a suite and then select one or more products.
- Select a suite, a product, and then select one or more streams.
- Click Delete and confirm.
- Reviews in Pulse are not deleted when their parent location is deleted. You can search for reviews and re-register the product and/or stream to browse to them.
- Deleting a suite unregisters its products and streams from Pulse but does not affect Dimensions CM.
- Unregistering a product unregisters its streams from Pulse but does not affect Dimensions CM.
- Unregistering a stream does not affect Dimensions CM. The stream is automatically re-registered in Pulse when deliveries are made to it in CM (unless the parent product is also unregistered).
- Delete a product or unregister a stream if you deleted the corresponding object in Dimensions CM and do not want it to appear in Pulse.
Modify a Suite or Product
Administrators can modify the title and description of suites and products.
- Open a suite or product.
- Click Edit.
- Modify the title and/or description.
- Click Save.
Favorite Streams
You can add, or remove, a stream from your list of favorite, active streams. Favorite streams are marked with a star and are always displayed at the top of the streams list.
- Open a stream.
- To the right of the stream name toggle the star to add, or remove, it from your favorites.
Move a Product to another Suite
Administrators can move a product to another suite.
- Open a product.
- Click Move.
- Select a suite from the list.
- Click Move.
Filter the List of Streams
On a product page you can filter the list of streams that is displayed.
- Open a product's home page.
- In the Streams section, in the search box type a filter. Pulse automatically displays a list of all the streams that match the string (not case sensitive).
Plan and Track Work
You can use backlogs, iterations, and requests to plan and track your team's work.
About Backlog Planning
Backlog planning enables you to organize your team’s work and group requests into common areas of work using a prioritized hierarchy of epics and features. An epic is a large unit of work that is typically broken down into smaller units of features and requests.
- Epics, features, and requests can only belong to one backlog, but you can move them between backlogs.
- Epic and features are optional and you can plan a flat backlog that only contains requests.
- Backlogs are located at the product level in Pulse.
- You can view a backlog as a hierarchy or a flat view.

About Requests
Requests are used to track and approve the changes your team is making. A request is a single unit of work, equivalent to a story in Agile planning, that can report a defect, suggest an enhancement, or detail other work for a particular product. You use story points to estimate the size of a request. Each request type has a lifecycle assigned to it that determines which users may work on the request.
The Request Catalog
The request catalog displays all the requests in a CM product. You can open any request and view its details.
- Select a product.
- On the sidebar click Request Catalog. Each row displays information about a specific request including its owner, lifecycle state, and any backlogs and iterations to which it belongs.
- To view a request's details, select it.
- General tab: displays information about the request, including:
- Associated reviews and changesets.
- The request's owners.
- Total and remaining story points.
- A burndown chart (if the request is included in an iteration).
- Any iteration or backlog to which the request belongs.
- Attachments.
- Attributes tab: each request type has different user defined attributes, which record important information about the request. For example, Estimated completed date, Raised by, and Severity. Some attributes may be required.
- Action History tab: displays information about when the request was actioned to different states in its lifecycle and the users that performed the action. To filter the action history, select a lifecycle state.
- General tab: displays information about the request, including:
Configure Request Types
Administrators can:
- Disable request types to constrain which ones can be used in request planning. However, at least one type must be enabled.
- By default all request types are enabled and their attributes are not mapped.
- Map Pulse attributes to CM request attributes, which enables them to be viewed and edited in other CM clients.
- Select the product where you want to enable request types.
- On the sidebar select Product Settings.
- Select Story Request Types. A list of all request types is displayed.
- Select the request type that you want to configure.
- Select or deselect Enable request type.
- Enable: existing requests of this type are visible and you can create new requests.
- Disable: existing requests of this type are visible but you cannot create new requests.
- In the Attributes Mappings section, optionally map Pulse request attributes to CM request attributes. Select CM attributes that best suit how your team uses request planning. For details see below.
- Click Save.
Mapping Pulse Attributes to CM
To enable Agile planning, Pulse requires additional fields, for example, tracking effort over time. You can store these fields in Pulse or map them to CM request attributes:
- If you store attributes (unmapped) in the Pulse database you do not need to add them to your process control plan in Dimensions CM. This allows you to evaluate and use Pulse more easily, especially if the fields will alway be edited in Pulse.
- If you map attributes to CM they can be viewed and edited in other CM clients.
| Pulse attribute | Description | Default mapping | Can be mapped to |
|---|---|---|---|
| Summary | A detailed description of the request. | Detailed description | Single-value character field or Detailed description |
| Acceptance Criteria | Specifies the criteria to be met before the story is considered to be complete. | Not mapped (stored only in Pulse database) | Single-value character field or Detailed description |
| Remaining Story Points | The estimated effort left to complete the request (in arbitrary units, such as story points). Used to generate the burndown charts. | Not mapped (stored only in Pulse database) | Single-value number field |
| Total Story Points | The total effort estimated to complete the request (in arbitrary units, such as story points). Used to generate the burndown charts. | Not mapped (stored only in Pulse database) | Single-value number field |
| Blocked | Specifies if a story is blocked and cannot be progressed. Often a Yes/No attribute. | Not mapped (stored only in Pulse database) | Single-value character field with a valid set that has at least two values. You must specify which value means Yes and which value means No. |
About Iteration Planning
An iteration is one development cycle, sometimes known as a sprint, which typically has a duration of a few weeks. An iteration includes the requests your team are confident they can complete before the duration ends. As an iteration progresses, the remaining effort required to complete the requests should decrease. You can view an iteration as a list or a card wall. Iterations are located at the product level in Pulse.
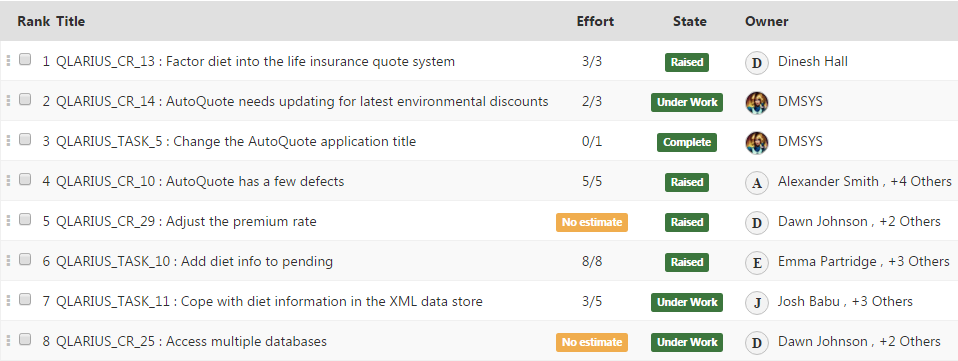
A list displays the content of an iteration in a flat list and includes information such as:
- What requests are being worked on.
- For each request, its rank order in the iteration, title, effort, current state, and owners.
- The progress of the work; the effort, in story points, required to complete each request.
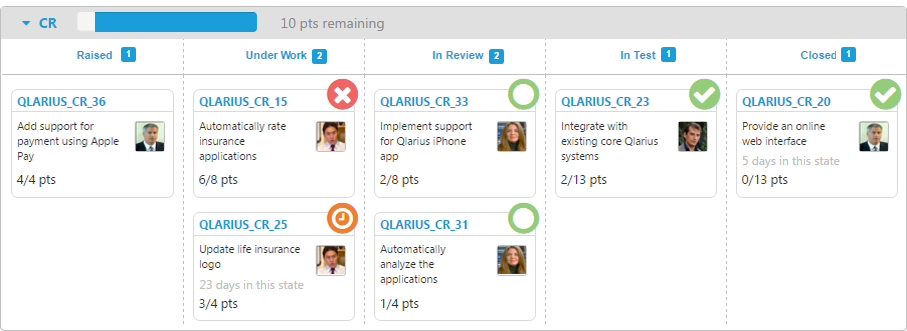
On a card wall each card displays information about a specific request such as:
- Which team member is working on it.
- The request’s story points.
- If the request is blocked.
- The number of days the request has been in its current state.
- A badge indicating its review state and the health of the changes.
Cards are grouped in rows by request type with a separate column for each lifecycle state.
A card wall also displays metrics about the progress of the current iteration:
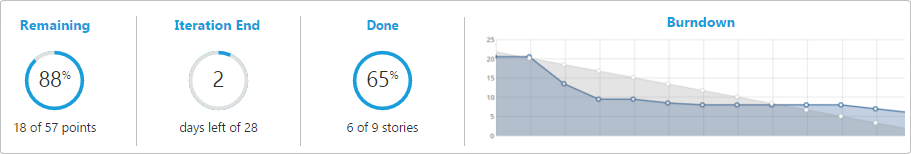
- In progress: story points remaining to be completed (as a number and percentage).
- Iteration end: the number of days left until the iteration ends.
- Done: stories completed (as a number and percentage).
- Burndown chart: helps to predict when the work will be completed.
Plan and Manage a Backlog
You typically start backlog planning by:
- Creating a new backlog.
- Optionally adding epics and features.
- Populating the backlog with work (requests).
Create a Request Backlog
If you are an administrator, you can create a new backlog and assign backlog owners. A backlog owner can manage its content, for example: add, remove, and rank items. The backlog owners can be changed by an administrator or another owner.
- Select the product where you want to create the new backlog.
- On the sidebar select Backlog.
- Click New.
- Give the backlog a name and summarize its purpose.
- (Optional) To assign one or more owners:
- Click Add. The Add Owner dialog box is displayed.
- In the Search box enter a string that matches registered Pulse users.
- Select one or more users and click Add Owner.
- Click Save.
Open a Backlog
- Select the product containing the backlog.
- On the sidebar select Backlogs.
- Select a backlog.
- You can show or hide:
- Planned stories that are already included in an iteration
- Request IDs
- Closed stories
- To display the requests as a flat, ranked list, click
 .
.
Create an Epic or Feature
- Open the backlog where you want to create a new epic or feature.
- (Optional) Click New and select Epic or Feature.
- Give the epic or feature a title and summarize its purpose.
- Click Save.
- Add additional epics and features as required.
- To change the hierarchy, drag and drop epics and features in the backlog.
Add a Request from the Request Catalog
You can add an existing CM request that originated from inside or outside your team.
- Open the backlog where you want to add a request.
- Click this button
 to split the view and select Request Catalog.
to split the view and select Request Catalog. - Select a request and drag it to a specific place in the backlog hierarchy.
- You can search for a request using various criteria, for example, title or ID.
- A backlog or iteration's label is displayed if the request is already included in one.
- The request catalog displays all the requests in the current CM product.
Create a New Request
You can create a new request in a backlog.
- Open the backlog where you want to create a new request.
- Optionally select the parent epic or feature that will contain the request. To add the new request at the top level of the backlog do not select an epic or feature.
- Click New and select a request type, for example, CR.
- On the General tab do the following:
- Give the request a title and summarize its purpose.
- For Acceptance Criteria specify the criteria to be met before the story is considered to be complete.
- For Story Points estimate the total number of points required to complete the work and the points remaining until will be finished. Story points are an estimation of a request’s relative complexity compared to other requests, and the effort required to complete it.
- On the Attributes tab specify or select values. Each request type has different attributes and some may be mandatory. The attributes are similar to those in the other CM clients.
- Click Save.
Move Epics, Features and Requests between Backlogs
You can move epics, features, and requests between backlogs. An object can only belong to one backlog; if you move one to the target backlog it is removed from the source backlog. When you move a feature its child requests are also moved.
- Open the backlog where you want to move an object to.
- Click this button
 to split the view and select Backlog.
to split the view and select Backlog. - In the search field enter the name of a backlog. You can search by title or ID.
- Select a backlog from the list.
- Select an epic, feature, or request and drag it to a specific place in the backlog hierarchy on the left.
- A backlog hierarchy automatically expands when you drag an object over it.
- You can also move objects from the backlog on the left to the one on the right.
Prioritize and Rank Requests in a Backlog
In each backlog, requests are ranked in descending order of priority in their parent epic or feature. You can rank and prioritize requests in the structured or flat view.
- Open the backlog where you want to prioritize and rank requests.
- Click this button
 if you want to display the flat view.
if you want to display the flat view. - Select a request and drag it to a different position in the hierarchy.
Mark a Request as Blocked
If you cannot continue working on a request you can mark it as blocked.
- Open the backlog containing the request you want to block.
- Select the request.
- Select Mark Blocked. In the backlog the request is now labeled as Blocked.
Delete an Epic, Feature or Request
You can delete an epic, feature, or request from a backlog. If you select an epic that has child features they are also removed. Any requests contained in an epic or feature are removed from the backlog and made available to the team.
- Open the backlog where you want to delete objects.
- Select one or more epics, features, or requests. Multiple objects that you select must be at the same level in the backlog hierarchy. For example, you can only select requests and features that are at the same level in an epic.
- Click Delete.
Plan and Manage an Iteration
Create an Iteration from a Backlog
You can create a new iteration from a backlog if you are an administrator or the backlog owner. The new iteration can only include requests that are not already assigned to another iteration. Requests that you can add have a green circle next to the their label ![]() . If you select an epic or feature, its child requests are included in the new iteration.
. If you select an epic or feature, its child requests are included in the new iteration.
- Open a backlog.
- Select one or more epics, features, and requests. Multiple objects that you select must be at the same level in the backlog hierarchy. For example, in an epic you can only select requests and features that are at the same level.
- Click Create Iteration.
- In the Create Iteration dialog box do the following:
- Give the iteration a name and summarize its goals.
- Specify the duration of the iteration and a start date.
- Click Save.
Create an Iteration from an Existing Iteration
You can create a new iteration containing requests from an existing iteration if you are its owner or an administrator. This is useful when you have finished a sprint and want to move uncompleted requests to a new iteration. The owner of the source iteration becomes the owner of the new iteration and the selected requests are moved to the new iteration.
- Select the product where you want to create the new iteration.
- On the sidebar select Iterations.
- Select the iteration that will be the source for the new iteration.
- Select one or more requests.
- From the Move To menu select New Iteration.
- In the Create Iteration dialog box do the following:
- Give the iteration a name and summarize its goals.
- Specify the duration of the iteration and a start date.
- Click Start.
Create a New Empty Iteration
If you are an administrator you can create a new, empty iteration.
- Select the product where you want to create the new iteration.
- On the sidebar select Iterations.
- Click New.
- Give the iteration a name and summarize its goals.
- Specify the duration of the iteration and a start date.
- (Optional) To add an owner:
- Click Add. The Add Owner dialog box is displayed.
- In the Search box enter a string that matches registered Pulse users.
- Select one or more users and click Add Owner.
- Click Save.
Open an Iteration
- Select the product containing the iteration you want to view.
- On the sidebar select Iterations.
- Select one of these tabs: Current, Future, Previous
- Select the iteration.
Add a Request from a Backlog
You can add a request from a backlog to an iteration if you are the owner of the iteration or an administrator. You can only add requests that are not already assigned to another iteration. Requests that you can add have a green circle next to the their label ![]() .
.
- Open the iteration where you want to add a request.
- Click the Content tab.
- Click this button
 to split the view and select Backlog.
to split the view and select Backlog. - Select a backlog from the list. You can also search by title or ID.
- Select a request and drag it to any position in the iteration.
Move a Request from another Iteration
You can move a request from another iteration if you are the owner of both iterations. The request is removed from the source iteration and added to the target iteration.
- Open the iteration where you want to add a request.
- Click the Content tab.
- Click this button
 to split the view and select Iteration.
to split the view and select Iteration. - Select an iteration from the list or search for an iteration by title or ID.
- Select a request and drag it to any position in the iteration on the left.
Prioritize and Rank Requests
In each iteration, requests are ranked in descending order of priority. To change a request's position, select it and drag to a different position.
Move Requests to another Iteration
You can move requests to another iteration if you are the owner of both iterations.
- Open the iteration from where you want to remove requests.
- Click the Content tab.
- Click this button
 to split the view and select Iteration.
to split the view and select Iteration. - Select a target iteration from the list or search for an iteration by title or ID.
- In the source iteration on the left select the requests that you want to move.
- Select Move To and then Iteration on Right.
Move Requests to a New Iteration
You can move requests from an existing iteration to a new iteration.
- Open the iteration from where you want to remove requests.
- Click the Content tab.
- Select the requests that you want to move.
- Select Move To and then New Iteration.
- Give the new iteration a name and specify its duration and start date.
- Click Start.
Edit an Iteration
You can edit an iteration if you are the owner or an administrator.
- Open the iteration that you want to edit.
- Click Edit.
- Edit the iteration.
- Click Save.
Remove Requests from an Iteration
You can remove requests from an iteration if you are the owner or an administrator. After you remove a request it can be added to other iteration.
- Open the iteration from where you want to remove requests.
- Select one or more requests.
- Click Remove and confirm.
Delete Iterations
You can delete one or more iterations if you are the owner or an administrator.
- Select the product containing the iterations.
- On the sidebar select Iteration.
- Select one of these tabs: Current, Future, Previous
- Select iterations.
- Click Delete and confirm.
View Request Details on the Card Wall
When the card wall is displayed you can quickly view a request's details.
- Open an iteration and display the card wall.
- Select a card. The request's details are displayed in a pane on the right.
Display Off-Normal Request States
You can display off-normal request lifecycle states, which are not displayed by default.
- Open an iteration and display the card wall.
- Select Display Settings, select Show off normal states, and click Apply. If the off-normal state column is collapsed, click this button:

Hide Charts
You can hide the charts at the top of a card wall to make more space for request types and cards.
- Open an iteration and display the card wall.
- Select Display Settings, deselect Show charts, and click Apply.
Action Requests
You can action a request to a new lifecycle state if it is in your Inbox or you are a Dimensions CM administrator.
Action a Request from a Backlog or Iteration
- Open the request that you want to action.
- Click Action To and select a lifecycle state from the list. The Action Request dialog box is displayed.
- On the General tab optionally modify the total and remaining story points.
- Click the Owners tab and optionally add users who will own the request after it is actioned:
- Click Add. A dialog box displays a list of all the users that can be added as owners.
- From the Role to assign list, select the role with which to assign the new owners, for example, Developer.
- From the Capability of users list, select a capability for the new owners. For more information see the Dimensions CM Process Configuration Guide.
- Select one or more users and click Add.
- When you action a request you may need to provide additional information on the Attributes tab, some of which might be required.
- Click Action.
Action a Request from a Card Wall
- Open the iteration containing the request that you want to action.
- Click the Card Wall tab.
- Drag a request to another lifecycle column. The Action Request dialog box is displayed.
- When you action a request you may need to provide additional information on the Attributes tab, some of which might be required.
- On the Owners tab, optionally select the user who will become the request owner after it is actioned.
- Click Action. The request’s state is changed and it moves to the next lifecycle column on the card wall.
Delegate a Request
Delegate a request when you want to assign it to other users. When you delegate a request you can change the role assignments for it, for example, Developer. You can also select a Dimensions CM capability, for example:
- Leader: sole responsibility for the request.
- Primary: primary responsibility for the request.
- Secondary: acts as a backup to the primary role.
- Open the request catalog and select the request.
- On the General tab, in the Owners section click Add.
- From the Role to assign list, select the role to be delegated to the users.
- From the Capability of users list, select a capability for the users.
- From the Users to assign section select one or more users.
- Click Delegate.
Edit Requests
You can edit a request's details if it is in your Inbox or you are a Dimensions CM administrator. After you edit a request its new values are displayed in all CM clients.
- Open the backlog or iteration containing the request that you want to edit.
- Select the request.
- Click Edit.
- Select the General tab and edit the values. You can also:
- Add and remove owners.
- Edit the story points.
- Add and remove attachments.
- Select the Attributes tab and edit the values. The attributes vary between request types but are the same as in the other CM clients. Each request type has different attributes. Attributes that are required for the next state are indicated.
- Click Save.
Review Work
About Reviews
Video: Introduction to Peer Review
You can use peer review to:
- Comment on, and review, the changes in your development projects.
- Collaborate with team members.
- Get insight into the health of changes in your changesets and streams, such as the results of expert chains.
- Promote team work and development best practices.
- Vote to approve or reject reviews, which may cause reviews to be marked as approved or sent for rework.
If you are a user with administrator rights you can also:
- Change a review's owner.
- Send a review for rework back to its owner.
- Change a review's state.
- Abandon a review.
The review list displays all the reviews that have been created for the selected user, suite, product or stream. A review page displays information about a specific change. You can control how a review's state is changed with the configurable review rules.
Reviews are also displayed on the activity feed for suites, products, streams, and on the user's Home page.
Review States
Pulse's review states and state changes are:
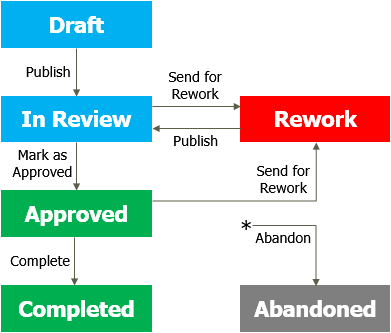
Reviewers vote to approve, reject, and abstain from a review. Depending on the configurable rules their votes may cause a state change, or contribute to a state change in the future. By default, the first reviewer to vote on a review changes its state but different rules may be configured in your environment.
The review states are:
- Draft: the review is being modified by the user who is the owner.
- In Review: the review has been published. Reviewers can add comments and vote on the review.
- Approved: the review's changes have been accepted.
- Rework: the review has been sent back to its owner with suggestions for improvement.
- Completed: if there are no issues the Approved review is normally marked as Completed by the owner.
- Abandoned: a review can be changed to Abandoned at any time by an administrator. The review is closed and removed from circulation.
Review Roles
A user can hold one of the following roles on a review:
- Owner: normally the user that delivered the changeset that created the review. The owner can be changed by an administrator to any valid user.
- Lead reviewer: can be assigned automatically from the changeset and modified manually. The valid lead reviewers are derived from the real role assignments on the design parts in Dimensions CM that own the items being reviewed. A lead reviewer can add optional reviewers.
- Optional reviewer: normally assigned manually. The valid optional reviewers are derived from the candidate role assignments on the design parts in Dimensions CM that own the items being reviewed. Optional reviewers cannot assign other reviewers.
Delivery filters control which changesets automatically create reviews. Dimensions CM role assignments on the items in the changeset determine which users are automatically assigned as lead reviewers or are available to be assigned as optional reviewers.
Review Rules
A change in a review's state is triggered by one of the following:
- A user with the appropriate role (Owner or Administrator) changes the review state manually.
- A decision made by a review rule that has run automatically.
The review rules are codified as a script that runs when one of the following significant events occur:
- A new changeset is associated with a review, which may automatically assign reviewers to the review.
- A user manually changes the state of a review.
- A reviewer votes to approve, reject, or abstain with no opinion on a review that is at the In Review state.
- The owner of a review is changed.
- The reviewers assigned to a review are changed manually.
- A request associated with a review is actioned to the In Review state in Dimensions CM. This may automatically assign reviewers.
A rule script uses the votes of the lead and optional reviewers, and additional information, to decide whether to change a review's state. You can create, or modify, scripts and set the default rule script for each stream.
If you are using the built-in defaultRule.js rule script the default behavior automatically changes the review state from:
- Draft to In Review when a reviewer is assigned.
- In Review to Approved or Rework after the first vote has been cast by any reviewer.
- Rework to In Review when the request's state changes to In Review in Dimensions CM.
The Review List
A review list displays the following reviews:
- Suites: reviews for all products and registered streams
- Products: reviews for all registered streams
- Streams: reviews for that stream only
To open the review list:
- Select a suite, product, or stream.
- On the sidebar select Reviews.
Each row in a review list is a separate review and includes the following information:
- The review's label (number and title)
- The date the review was created
- The stream associated with the review
- The user who created the review
- The review's current state (mouse over the icon to display)
You can select a filter to modify the type of reviews that are displayed.
- Open a review list.
- From the Reviews list select a filter.
You can also sort the reviews by category, and in ascending or descending order.
- Open a review list.
- Click Sort by.
- Select a category.
- Optionally select, or unselect, Sort descending.
Review Pages
A review page displays the following information:
- The review ID and title.
- The associated stream or project.
- A summary of changes to the review such as: the results of expert chains, comments that have been made, changes to the review's state, and votes by reviewers.
- The review owner and the lead and optional reviewers. If you are a lead reviewer, and a review is at the In Review state, you can add and remove optional reviewers.
- Related Dimensions CM change requests.
- The results of experts that ran on the changesets.
- The associated changesets. Multiple changesets are associated with a review if users have made several deliveries to a stream using the same request.
- A list of all the files associated with the changesets.
- The contents of the files.
Changes to files and folders, and to lines and characters in files, are displayed visually:
- Green background: added
- Red background: deleted
- Yellow background: changed
You can show an entire file or only the changes that have been made to it.
View File Content
The contents section and the sidebar display all the files and folders in the review.
- The sidebar displays the total number of files in the review:
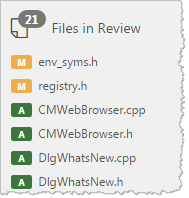
- The Contents section displays the number of files that have been added, modified, and deleted.
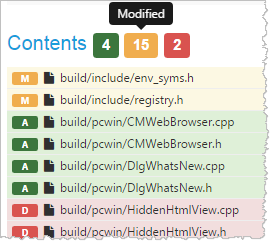
Click a file or folder to view its contents.
If a review is associated with multiple changesets you can filter the files that are displayed.
- In the Changesets section select two changesets to compare with each other.
- Click View. The contents section and the sidebar are updated and only files that have changed between the selected changesets are now displayed.
- Binary files cannot be displayed but you can download them onto your machine.
- If a file is marked as binary, but you know it is a text file, from the Show menu select As Text. In CM, check the format and upload rules.
- If only part of a file's contents are displayed, from the Show menu select Entire File.
- Only the contents of the first 30 files are displayed. To load a file scroll down to it and click Load File.
- To display the previous revision of a file, from the Show menu select Previous. The current version is displayed in the right column and the previous version in the left column.
Related CM Requests
Related CM requests are displayed in the Requests section. Click a review to view its details.
Watch a Review
You can optionally watch a review when it is at specific states. When changes are made to the review you will be notified by email. You can select the notifications that you receive.
- To watch a review click Watch.
- To stop watching a review click Unwatch.
Publish a Review
When a review is created its initial state is Draft. If you are the review owner, or a user with administration privileges, you can publish the review so that it is available to your team. The owner is normally the user that delivered the changeset that created the review.
- On the review list page select the review you want to publish.
- Click Publish.
- Click Publish Review. The review is now at the In Review state.
Add and Remove Reviewers
Each review can have reviewers with these roles:
- A review owner; normally the user who delivered the changeset that created the review.
- One or more lead and/or optional reviewers.
- A review owner, or an administrator, can add and remove lead and optional reviewers.
- A lead reviewer can add and remove optional reviewers.
- An administrator can add anyone as a review owner or a reviewer.
- A review owner or lead reviewer can only add reviewers that have a role on one of the review items' design parts.
To add reviewers to a review:
- Open a review.
- In the Reviewers section click Add and then Lead Reviewer or Optional Reviewer.
- Select more or more reviewers.
- Control click to select multiple users.
- Use Search to find users.
- Click Add Reviewers.
To remove reviewers from a review:
- Open a review.
- In the Reviewers section select more or more reviewers.
- Click Remove and confirm.
Add Comments to Files in Reviews
You can add comments to specific files in a review and collaborate with team members. This is different to adding a comment to an entire review.
- On a review page find a file.
- The files in a review are listed in the Contents section and the sidebar.
- The current version of a file is displayed in the right column and the previous version is displayed in the left column.
- In the left or right column click and drag to select the line numbers where you want to add a comment.
- In the Comments box enter your comments.
- Optionally format the comment (see the markdown reference).
- To display how your comment will look click Preview.
- To continue editing click Edit.
- To add the comment click Comment. Your comments are now visible to your team and responses are displayed in the same comment box.
- Comments are only displayed on review pages and are not added to files.
- You can add comments when a review is at specific states.
- You can edit your own comments until there is a reply.
Vote on a Review
You can vote to approve or reject a review. Depending on how the rules script for this stream is configured, your vote may trigger the rule script to move the review to its next state.
- At the top of a review click Approve or Reject.
- Enter the reasons why you are voting to approve or reject the review.
- Optionally format your comment (see the markdown reference).
- To display how your comment will look click Preview. To continue editing click Edit.
- If a check list is presented, select items that have influenced your voting decision.
- Click Approve or Reject.
You can also abstain from voting. This useful if there is a rule that mandates that all reviewers must vote, but you have no opinion.
- Open a review.
- Click Action
 and select Abstain with No Opinion.
and select Abstain with No Opinion. - Enter a reason for abstaining and click Abstain.
Mark a Review as Approved
If you are a user with administrator privileges you can bypass reviewer voting and mark a review as Approved.
- Open a review.
- Click Action
 and select Mark as Approved.
and select Mark as Approved. - Click Approve Review.
Change a Review’s Owner
If you are a user with administrator privileges you can change a review's owner.
- Open a review.
- Click Action
 and select Change Owner.
and select Change Owner. - Select a user.
- Click Change Owner.
Send a Review for Rework
If you are a review owner, or a user with administrator privileges, you can send a review back to its owner for rework with suggestions for improvement, and bypass reviewer voting.
- Open a review.
- Click Action
 and select Send for Rework.
and select Send for Rework. - Click Send for Rework.
Abandon a Review
If you are a review owner, or a user with administrator privileges, you can abandon a review. Abandoning a review indicates that it is no longer active and stops further review activity. This action cannot be reversed.
- Open a review.
- Click Action
 and select Abandon Review.
and select Abandon Review. - Click Abandon Review.
Close a Review
If you are a review owner, or a user with administrator privileges, you can close a review. Closing a review prevents further changes being made to it. Only close a review if you are sure that no further work is required.
- Open a review.
- Click Close Review and confirm.
Comment on a Review
You can add comments to an entire review when it is at specific states. Comments appear in a review's activity feed. This is different to adding comments to a specific file in a review.
- Open a review.
- Click Action
 and select Comment on Review.
and select Comment on Review. - Optionally format your comment. To display how your comment will look click Preview. To continue editing click Edit.
- When you have finished click Add Comments.
Edit a Review's Title
You can edit a review's title.
- Open a review.
- Click Action
 and select Edit Title.
and select Edit Title. - Enter a new title and click Save.
Customize Review Page Defaults
You can customize how the following elements are displayed on your review pages:
- Comments
- Whole file
- Previous versions of a file
You can also select a white space option for viewing file differences, for example, Ignore Trailing White Space.
- Open a review.
- Click Action
 and select Display Defaults.
and select Display Defaults. - From the Visible Elements select options.
- From the White Spaces list select an option.
- Click OK.
Check the Health of Work
About Health and Quality
Pulse enables you to check the health and quality of the changes in your software products. You can:
- Visualize streams, branches, and merges.
- Run expert chains to check the health of source code and builds.
- Review changes to determine if they are ready to be merged or released.
- Run reports to display statistics and trends in your streams.
About Changesets
Pulse uses Dimensions CM changesets to visualize information about changes. A changeset is a logical grouping of changes that is automatically created every time you deliver changes in a stream or project to a Dimensions CM repository. A changeset enables you to identify, work with, and track, sets of changes. Every changeset that you deliver creates a new version of a stream or project.
Video: Introduction to Changesets
View Changeset Information
There are multiple ways that you can view the information in changesets:
- Changeset Graph: visualizes your changesets and streams of development.
- History view: displays the history of changes in chronological order.
- Contributors view: displays all the developers who have made deliveries to the repository.
- Punch Card view: displays the busiest delivery periods by the day of the week and time.
You can view changeset information for suites, products, and streams. The Home page displays changeset information specific to the user who is currently logged in.
Filter Changeset Information
You can filter the changeset graph, or any information view, to:
- Limit the data that is displayed.
- Focus on a specific feature or set of streams and projects.
- Focus on a specific period of time.
- Select a suite, product, or stream.
- Open the changeset graph or one of the information views.
- At top right click the date filter.
- In the Stream Name box enter a wildcard to match stream and project names, for example: QLARIUS:JAV*
- You can enter multiple wildcard strings; separate each wildcard with a comma.
- To hide specific streams, add a minus '-' character at the start of the string, for example: -*JAV*
- To only display streams that you have marked as favorites, select Show favourites only.
- From the Start Date and End Date lists do one of the following:
- Select a predefined date range.
- Select Since or Until and use the date picker to manually select a date range.
- Start Date displays all data that matches the wildcard from the date that you specify.
- End Date displays all data that matches the wildcard up to and including the date that you specify.
- Click Apply. The graph or view refreshes and only displays data that matches the filters that you specified.
View Changesets on a Graph
Overview
A changeset graph visualizes streams and their change history across multiple releases A graph provides development teams and release managers with a visual understanding of what changes are being worked on, where, and why. Experts provide feedback on the health of changes and an indication of release readiness.
A changeset graph enables you to:
- Visualize all your streams and projects in one place including branches and merges. Each circle or group represents a changeset or a group of changesets.
- Review the health and readiness of your changesets and determine if they are ready to be merged or released.
- Watch in real time as streams are branched, merged, and moved through the lifecycle.
Changeset health is displayed visually:
 Grey circle: the changeset has no associated expert results
Grey circle: the changeset has no associated expert results
 Yellow circle: the expert results have warnings
Yellow circle: the expert results have warnings
 Red circle: the expert results have errors or an expert may have failed
Red circle: the expert results have errors or an expert may have failed
 Green circle: the expert results are successful
Green circle: the expert results are successful
 Purple circle: an expert has aborted
Purple circle: an expert has aborted
 Orange circle: an expert run has been requested or is in progress
Orange circle: an expert run has been requested or is in progress
 Tick (inside a circle or group): the review was marked as approved
Tick (inside a circle or group): the review was marked as approved
 Cross (inside a circle or group): the review was sent for rework
Cross (inside a circle or group): the review was sent for rework
 Clock (inside a circle or group): an expert chain is in progress
Clock (inside a circle or group): an expert chain is in progress
 Solid small circle (inside a circle or group): the changeset has a review
Solid small circle (inside a circle or group): the changeset has a review
 Hollow small circle (inside a circle or group): the changeset does not have a review
Hollow small circle (inside a circle or group): the changeset does not have a review
 Blue circle: the changeset is selected and its details are displayed below
Blue circle: the changeset is selected and its details are displayed below
Display a Changeset Graph
- Select a suite, product, or stream. The graph is scoped to the suite, product, or stream that you select.
- On the sidebar select Changeset Graph.
- (Optional) Filter the information that is displayed.
Using the Changeset Graph
- Mouse over a stream's label to display its changeset history.
- Click a stream's label to display an overview.
- Mouse over, or select, a changeset to highlight all the merge lines that connect it to other changesets.
- Control-click changesets to highlight multiple merges.
- Mouse over a changeset to display a summary.

- Mouse over a changeset group to display the stream version range, and the result of the expert chains that ran on the most recent changeset.
View Changeset Details
Click a changeset to view more details. A pane at the bottom displays information including:
- The changeset number and description.
- The stream or project version that owns the changeset.
- The user whose delivery created the changeset.
- The date and time the changeset was created.
- The review created by the delivery. Mouse over to display its current state.
- The result of the expert chain that ran on the changeset.
- Control-click to select and view the details of multiple changesets.
- Click a review to open the review page associated with a changeset.
- (Administrators only) If a changeset did not create a review automatically, click Create Review to create one manually.
Group Changesets
You can view changesets individually or grouped by days or weeks. Groups take up less space on the graph and look like this:
 The number of changesets contained in a group is displayed at the top right.
The number of changesets contained in a group is displayed at the top right.
- Open the changeset graph.
- From the Changesets Graph list select one of the following:
- Individual Changesets
- Grouped by Days
- Grouped by Weeks
View Changeset History
The changeset history view displays changes to suites, products, and streams in chronological descending order. For each changeset the following information is displayed:
- The changeset number and description. Click to open the changeset page.
- The stream or project version that owns the changeset.
- The user whose delivery created the changeset. Click to open their Home page.
- The date and time the changeset was created.
- The review created by the delivery. Mouse over to display its current state. Click a review to open the review page associated with the changeset.
- The changeset's health.
- Select a suite, product, or stream. The view is scoped to the suite, product, or stream that you select.
- On the sidebar, select Changeset History.
- (Optional) Filter the information that is displayed.
View Changeset Pages
A changeset page displays information about a specific changeset including:
- The changeset ID and title.
- A summary of events such the results of expert chains and reviews that were created.
- A link to the review.
- The results of experts that ran on the changeset.
- A list of all the files in the changeset.
- The contents of the files.
- Select a suite, product, or stream.
- On the sidebar, select Changeset History.
- Select a changeset to open it.
Customize Changeset Page Defaults
You can customize how the following elements are displayed on all changeset pages:
- Comments
- Whole file
- Previous versions of a file
You can also select a white space option for viewing file differences, for example, Ignore Trailing White Space.
- Open a changeset page.
- Click Action
 and select Display Defaults.
and select Display Defaults. - From the Visible Elements select options.
- From the White Spaces list select an option.
- Click OK.
Display Delivery Activity
You can display the days and hours when deliveries were made to CM. Larger circles indicate higher activity.
- Select a suite, product, or stream. The view is scoped to the suite, product, or stream that you select.
- On the sidebar select Punch Card.
- (Optional) Filter the information that is displayed.
List who has Made Deliveries
You can display the developers who have contributed deliveries to CM in descending order (high to low). The colors on each horizontal bar represent the states of the experts that ran on the changesets:
- Green: success
- Yellow: unstable
- Red: failure
- Blue: no experts ran
Mouse over a colored section of a contributor's bar to display its percentage of the total number of changesets that have been delivered. The contributor's total number of deliveries is displayed to the right of their bar. The total number of contributors and deliveries for all developers is displayed at the top of the page.
- Select a suite, product, or stream. The view is scoped to the suite, product, or stream that you select.
- On the sidebar select Contributors. A list of contributors is displayed.
- (Optional) Filter the information that is displayed.
About Experts
Experts examine source code and built artefacts and report back any findings. The set of experts available in Pulse can be extended or updated by installing plug-ins. Experts are triggered when a delivery is made to a stream or according to a schedule, or can be triggered manually. You can configure experts to run in a sequence, called an expert chain. You can configure multiple independent chains to run on a stream, for example, the first chain runs on every delivery and performs brief static analysis. A second chain runs at midnight every day and performs more thorough analysis and deployment.
Expert Attributes
Experts have these attributes:
- Execution state: Success, Failure, Unstable, or Aborted.
- Measurement: A set of single-valued judgments about source code. For example, 24,847 might be a measurement of lines of code, and High might be a measurement of the security risk level.
- Finding: When issues are identified, experts annotate the source code and provide a "severity" level to indicate how serious an issue is. Annotations are displayed in tabular form in the Experts section of a review page and some experts also annotate the files in the Contents section. Some findings may include a link to a web page that provides more details. See Inspect Expert Results.
Experts Included with Pulse
The following experts are included with Pulse:
- Changeset Summary: counts the number of files added, deleted, and modified in each changeset. Does not have any configuration parameters.
- Checkstyle: enforces coding standards.
- Jenkins: a continuous integration server that you can use with Pulse to execute, and report on, builds of changesets as they are delivered.
- Kiuwan: measures, analyzes, and verifies the quality of your code.
- PMD: analyzes source code and finds common programming bugs.
- SDA Deployment: imports and deploys a component using Serena Deployment Automation.
- SDA Generic Process: runs a generic process in Serena Deployment Automation.
- SonarQube: inspects the quality of your code.
- Dependency Vulnerabilities: finds third party dependencies in your code that may have known security vulnerabilities.
- CM Build: if your team uses Dimensions Build and you have existing build configurations, you can run the configurations in Pulse.
- Halt on Failure: stops the chain if the previous expert in the chain failed. Does not have any configuration parameters.
- Script: Runs a batch file (Windows) or shell script (other operating systems).
- HP Fortify SCA (Static Code Analyzer): analyzes your source code and identifies the root causes of security vulnerabilities.
- WhiteSource: identifies all the open source components and dependencies in your build, reports any known security vulnerabilities, and lists their licenses.
For details about each expert and how to configure them see Configure Experts.
To add an expert to a chain see Create Expert Chains.
List all Expert Chains
To view all the expert chains that have been configured for a stream, select a stream, and on the sidebar select Expert Chains. Each chain displays the status of the most recent run.
Create and Configure Expert Chains
Administrators can create expert chains and add, and configure, multiple experts.
- Select a stream where you want to create an expert chain.
- On the sidebar select Expert Chains.
- Click New Expert Chain.
- In the Title box enter a description of this expert chain.
- On the Note tab optionally enter additional information about the chain.
- To configure the expert chain do the following:
- Schedule when the chain will run.
- Specify which streams will be analyzed
- Add and configure experts
- Set a log retention policy
- Save the new expert chain.
Schedule a Chain
- Select the When to Run tab.
- From the Schedule list select how often the chain will run, for example, when every changeset is delivered to the stream, or every hour at 30 minutes past the hour. To only start the chain manually select Never.
- To restrict when this expert chain runs, in the Matching Paths field enter Ant patterns. To trigger the chain, at least one path in the changeset must match the pattern. Enter one pattern per line or leave blank to run the chain on all changesets.
- In the Required capabilities field enter the machine capabilities (one per line) required by this expert chain, for example: Java
Only machines that match the requirements will run this chain. Leave blank to run this expert chain on any machine.
Specify Streams to be Analyzed
- Select the What to Analyze tab.
- To limit the content that is fetched from the stream when this expert chain runs, enter Ant style patterns to include specific paths. Enter one pattern per line or leave blank to include all the stream's content.
Add and Configure an Expert
- Select the Experts in Chain tab.
- From the Add Expert list select an expert.
- Add a name for this step in the expert chain.
- Configure the expert you just added. Each expert has different parameters, some of which are mandatory. For details about each expert, and how to configure them, see Configure Experts.
- Add and configure more experts as required.
- To change the running order of experts on the chain, drag and drop experts into different positions.
- To remove an expert from the chain, select it and click Remove.
Set a Log Retention Policy
- Select the Retention Policy tab.
- Select a retention policy for all the logs in this chain. Retention policies are configured by your administrator.
Inspect Expert Results
Expert results include:
- The name of the expert.
- The expert's run state, for example: Success, Running, or Failure.
- A summary of the findings including the name of the expert chain, the changeset number, and the stream or project name.
- The review where the chain ran (click to open it).
- The time taken to run the expert.
- A link to the expert's web page (where applicable).
You can inspect an expert's results in any activity feed or review page.
- Select a suite, product, or stream.
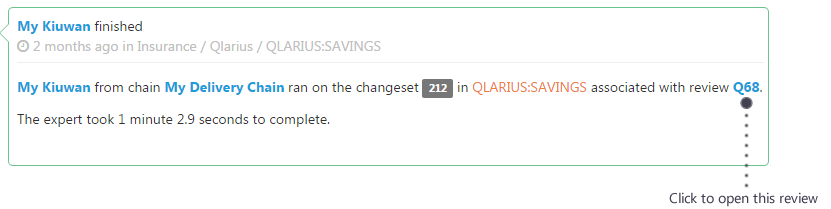
- Scroll down the Activity feed until you find an expert that you want to inspect. A typical expert result looks like this:
- To display the expert's full results click the review link. The review page opens.
The Experts section displays results for all the experts that ran on this review. Expand each expert to view its findings. Some experts may include a link to a web page that provides more details. A typical Experts section looks like this:
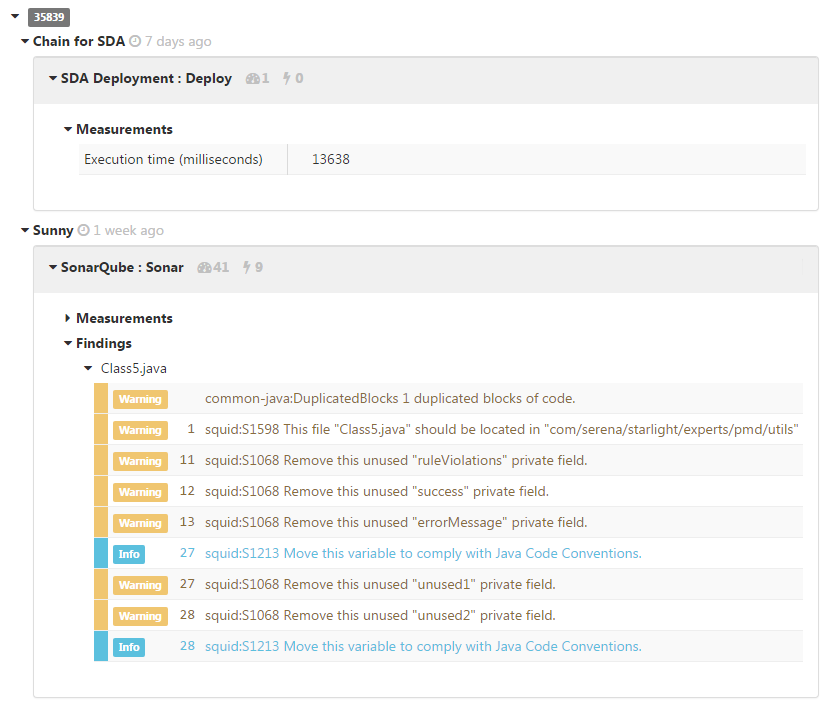
The Contents section of a review displays a list of all the files in the review and the number of expert findings for each file. A typical Contents section looks like this:
- To view an expert's findings for a specific file, in the Contents section select the file.
- From the Show menu select Show Entire File.
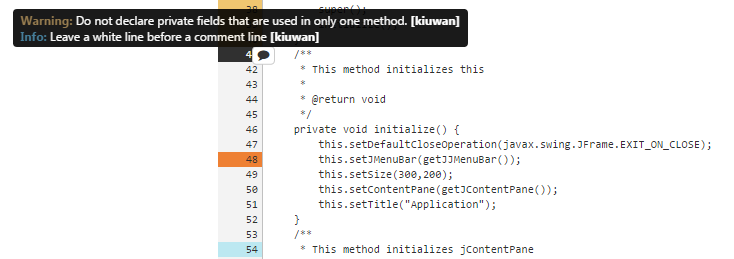
- Scroll down the file until you see results that you want to inspect. Each line number with a result has a color that represents one of these categories:
- Blue: information
- Dark Orange: error
- Orange: warning
A line may have multiple results.
- Mouse over a line number to display information.
View Expert Chain Logs
You can display the most recent runs of an expert chain and view the log for each run.
- Select a stream.
- On the sidebar select Expert Chains.
- Select an expert chain.
- The Runs tab displays the last six runs for the expert chain and includes:
- The status (succeed, fail, etc).
- The ID of the output log.
- The changeset where the expert ran (click the link to view its details).
- To view the output log click its ID.
- To filter the information that is displayed select a log threshold level. Default: Info
- To override the default log retention policy for this expert chain and keep the log, click Keep Forever.
Edit and Delete Expert Chains
Administrators can edit and delete expert chains:
- Select the stream containing the expert chain that you want to edit or delete.
- On the sidebar select Expert Chains.
- To delete one of more expert chains, select them from the list, click Delete, and confirm.
- To edit an expert chain, select it, and click Edit.
- Edit the chain's settings, add and remove experts, and change their running order (see details).
- Save the changes.
- Activity events involving the deleted chain.
- Findings or measurements that the deleted chain added to reviews.
- Any panels that contain measurements from the deleted chain.
About Reports
Reports display statistics and trends that are generated from the activity in your streams. Reports are scoped to the suite, product, or stream from where you run them. If you are an administrator you can create and manage reports.
- Suites can only run reports created at the suite level.
- Streams can run all reports created at all levels.
Run a Report
- Select the level at which you want to run the report (a suite, product, or stream).
- On the sidebar select Reports.
- From the Reports list select a pre-defined report.
- (Optional) Select a time period for the report (start and end dates).
- To refresh the report click Refresh.
Create Reports
You can create a new report and add multiple panels. Each panel can have one of the following:
 |
Metric: a chart with a single value, for example, the number of deliveries made. |
 |
Line Chart: an illustration of data points at successive time intervals. Mouse over a time interval to display the data for each value. |
 |
Pie Chart: a circular statistical graphic that is divided into sectors to illustrate numerical proportion. Mouse over a sector to display its value. The value in the middle is the first metric's numeric value as a percentage of the total. |
 |
Bar Chart: a diagram in which the numerical values of variables are represented by the height or length of lines, or rectangles of equal width. |
 |
Table: a set of data arranged in rows and columns. |
- Select the level where you want to create the report (a suite, product, or stream).
- On the sidebar select Reports.
- From the Actions menu and select Create View.
- In the Title box enter a name for the new view.
- In the Note box optionally enter information about the report.
- Click Save.
- To add a panel to the report do the following:
- Click Add panel.
- Enter a name for the panel.
- Select a display type.
- Select Report on difference from previous value to show how a value has changed over time. For example, to show a trend such as the number of defects.
- Select a width for the display (as a percentage of the width of the main window).
- Select one of these metric types:
- Review Metrics
- Expert Metrics (only available for streams)
- Click Add metric and select one from the list. You can add multiple metrics to these display types: pie charts, bar charts, and tables.
- Click Save.
- To add more panels repeat the previous step.
- Drag and drop panels to change their positions in the report.
Manage Reports
Administrators can delete and edit reports.
- Select the suite, product, or stream where the report is located.
- On the sidebar select Reports.
- From the Reports list select a report.
- To delete the report, from the Actions menu select Delete and confirm.
- To edit the report's title and description, from the Actions menu select Edit Title & Notes.
- To edit a report panel click Edit in its title bar. Modify the settings and click Save.
- To remove a panel click Delete in its title bar and confirm.
- Drag and drop panels to change their position in the report.
Create Reviews and Run Expert Chains
Overview
Administrators can configure changesets to automatically create reviews and run expert chains. The first delivery of a changeset to Dimensions CM creates a new Pulse review whose title is the same as the delivery change comment. If the review is related to a specific request, subsequent deliveries that use the same request are grouped under the same review.
Create Delivery Filters
Delivery filters enable administrators to control how reviews are created, and expert chains are triggered, for each stream. Every path in a changeset is matched against the patterns in a stream's delivery filter. If one or more paths pass through the filters, the changeset delivery creates reviews and runs expert chains. The default delivery filter for a product is used by any streams in that product that do not have an assigned delivery filter.
- Select the product where you want to create a delivery filter.
- On the sidebar select Delivery Filters.
- Select New Delivery Filter.
- In the Title box enter a name for the new delivery filter.
- In the Note box optionally enter information about the filter.
- Use the Changeset Path Filtering section to control which paths create reviews and run expert chains.
In the Include these paths box do one of the following:- To only create reviews and run expert chains for specific paths, enter Ant style patterns (one pattern per line),
for example:
**/*.java**/*.jsp - To create reviews and run expert chains for all changesets, leave blank.
- To prevent specific paths from creating reviews and running expert chains, enter
Ant style patterns (one pattern per line), for example:
**/.DS_Store**/tmp/** - To create reviews and run expert chains for the included changesets, leave blank.
- To only create reviews and run expert chains for specific paths, enter Ant style patterns (one pattern per line),
for example:
- If you have a system that delivers changes using specific user names, for example a build process, you can ignore
those changesets. In the Exclude changesets delivered by these users box enter the user names (login IDs)
on separate lines. For example,
regbuildexcludes all deliveries by the user with the login ID regbuild. Leave this box blank to disable it. - To ignore changesets with specific text in their delivery comments, in the Exclude changesets with these
messages box enter message patterns, where
*is a wildcard character and each pattern is on a separate line. For example,*NO_REVIEW*excludes deliveries where the message contains the keyword NO_REVIEW. Leave this box blank to disable it. - Click Save.
- To make this the default delivery filter for this product, on the Delivery Filters page select the filter. Click Set As Default and then Make Delivery Filter Default. A product can have one default delivery filter.
Automatically Create Reviews and Run Expert Chains
Administrators can configure which changesets delivered to streams automatically create reviews and run expert chains.
- Select the stream that you want to configure.
- On the sidebar select Stream Settings.
- To control which changesets delivered to this stream create reviews and run expert chains, apply a delivery filter:
- Select Filter Changesets using Delivery Filter. If you want all changesets that are delivered to this stream to create a new review and run expert chains, do not select this option.
- From the Delivery Filter list select the product's default filter or any other filter.
- To enable all changesets that pass through the selected delivery filter to create new reviews, select Create/Attach to a Review. If you do not want to create reviews, do not select this option.
NOTE If an existing review is associated with a Dimensions CM request, a new changeset is attached to that review (instead of creating a new one) when the following conditions are met:
- The review is at the Draft or Rework state.
- The review has the same owner as the user delivering the new changeset.
- The changeset uses the same request, or has the same review label, in its changeset delivery message.
- The changeset is associated with the same stream.
- To specify a review check list to be used with new reviews created in this stream, from the Review Check List To Use list select the product's default review check list or any other list. You can also choose not to use a check list with this stream.
- To specify the review rules for this stream, from the Review Rules To Use list select the product's default rule or any other rule.
- Click Save.
Diagnose Expert Chains
If you are having issues with an expert chain you can diagnose it by running it manually (administrator rights are required).
To diagnose the latest changeset
Select the stream that contains the expert chain that you want to diagnose and do one of the following:
- On the sidebar select Expert Chains, select the expert chain, and click Run on Latest Changeset.
- On the sidebar select Changeset History, select the latest changeset, and from the Actions menu select Run Expert Chains.
To diagnose a specific changeset
- Select the stream that contains the expert chain that you want to diagnose.
- On the sidebar select Expert Chains.
- Select the expert chain.
- On the Runs tab select a specific run.
- Click Re-run.
Set User Preferences
Subscribe to Review Notifications
You can select the review email notifications to which you are subscribed. Notifications are sent when an event takes place on a review, for example:
- A review that you own changes state.
- You become the owner of a review or are added as a reviewer.
- A review that you own is voted on.
- A review that you own is commented on.
- On the top navigation click Home.
- On the sidebar select Email Subscriptions.
- Select, or unselect, review notifications.
- Click Save.
Set Changeset Graph Defaults
You can set defaults for how the changeset graph is displayed.
- On the top navigation click Home.
- On the sidebar click Preferences.
- In the Changeset Graph Defaults section, from the Display Scale list select one of the following:
- Changeset: display individual changesets.
- Daily: groups changesets by days.
- Week: groups changesets by weeks.
- Select a Zoom Level.
- Click Save.
Set View Defaults
You can set defaults for how Views are displayed. Views include Reports, the Changeset Graph, Changeset History, Contributors, and Punch Card.
- On the top navigation click Home.
- On the sidebar click Preferences.
- In the Default Time Period for Views section select the default Start Date and End Date range for the data that is displayed.
- Click Save.
Administer Pulse
To administer Pulse you must be logged in as a user with administrator privileges.
Configure the Avatar Server
Administrators can configure where Pulse obtains user avatar images.
- On the top navigation click Administration.
- Select Avatars.
- Select one of the following sources for avatar images and user information:
- Disabled: all avatars display the default user picture.
- Serena Business Manager: use an SBM server to find avatar images and full names. Set the SBM server.
- LDAP Server: use the LDAP settings, see below.
- Gravatar: use an email address suffix. Set the suffix.
- If you selected LDAP, specify the following information:
- Server URL
The URL of the LPAP server, for example:
ldap://domain-controller.example.com:389 - Username
The bind user to perform searches as, for example:
cn=binduser,ou=Organizational Unit 1,ou=Organizational Unit 2,dc=example,dc=com - Password
The password of the LDAP bind user. - Base DN for search
The base DN to search from, for example:
dc=example,dc=com - Avatar image attribute
The LDAP attribute containing avatar image data, for example:
thumbnailPhoto - Follow LDAP referrals
To enable searches to follow LDAP referrals, toggle Follow LDAP referrals to Yes. - Search filter
The LDAP search filter to match objects, for example:
(&(objectClass=person)(sAMAccountName={0}))
- Server URL
Configure Special Services
Administrators can configure the servers that provide specialized services to Pulse, such as Serena Business Manager.
- On the top navigation click Administration.
- Select Servers.
- In the Serena Business Manager URL box enter the URL for the SBM user workspace, for example:
http://sbm-server.example.com/tmtrack/tmtrack.dll? - In the Email Address Domain Suffix box enter the suffix that is automatically appended to user names to form email addresses, for example:
@example.com. - Click Save.
Administer Email Notifications
Administrators can manage the review email notifications that users can subscribe to, and unsubscribe from. If a notification is disabled, users will not see the notification listed in their subscription preferences. If a notification is available, users can choose to subscribe to it.
- On the top navigation click Administration.
- Select Notifications.
- For each notification type select one of the following:
- Disabled: the notification is not available for users to subscribe to.
- Send notification: the notification is sent to users by default though they can unsubscribe from it.
- Do not send notification: the notification is not sent to users by default though they can subscribe to it.
- Click Save.
Manage Review Check Lists
When a user votes to approve or reject a review they are typically required to select items from a check list. Administrators can create different types of check lists to satisfy different levels of severity. For example:
- Secure: a complex check list with high levels of tightly controlled compliance, for example, for licensing.
- Minimum: a small list with low levels of compliance, for example, for in-house testing.
For each stream the same check list is used for approvals and rejections, however, you can associate a different review check list with each stream.
To create a review check list:
- On the top navigation click Administration.
- Select Review Check Lists.
- Click New Check List.
- Enter a name for the check list.
- Enter items that you want your reviewers to select when voting to approve or reject reviews. Review check lists may contain up to ten items. For example:
- Coding standards
- Export compliance regulations
- Software complexity rules
- Click Save.
To delete review check lists:
- Select Administration | Review Check Lists.
- Select one or more check lists.
- Select Delete and confirm.
You can also select the default check list for a product.
Manage Users
A user can be one of the following:
- Standard: can use peer reviews, changeset views, and request management.
- Administrator: can change a user's type and administer the system. There can be multiple administrators.
- On the top navigation click Administration.
- Select Users. A list of all the currently registered users is displayed including their user name, full name, email address, and user type.
- Select one or more standard users. From the Actions menu select Add administrator privilege.
- Select one or more administrators. From the Actions menu select Remove administrator privilege.
Keep Expert Chain Logs
By default expert chain logs are kept for 30 days. Administrators can create custom retention policies and apply them to expert chains.
- On the top navigation click Administration.
- Select Retention Policies.
- Click New Retention Policy.
- Enter a tile and description for the retention policy.
- Specify the number of items to be retained in the log, for example: 100
- Specify how many days items in the log will be retained, for example: 365 (one year)
- Specify the maximum size of the log in megabytes, for example: 1024 (a gigabyte). When the log reaches the defined size the oldest items will be purged.
- Click Save.
Manage Experts
Administrators can check what experts are installed, enable and disable experts, and view the results of recent runs.
- On the top navigation click Administration.
- Select Experts. The Experts page displays all the experts that are currently installed in your CM environment.
- (Optional) For each expert do the following:
- Enable or disable the expert.
- View the last runs.
A set of experts is installed with Pulse. For details about installing additional experts see the Dimensions CM Administrator's Guide.
Add and Modify Connections to CM Repositories
Administrators can add and modify connections to multiple repositories (Dimensions CM base databases).
- On the top navigation click Administration.
- Select Repositories.
- Do one of the following:
- To add a new repository select New Repository.
- To edit the connections for an existing repository, select it from the list. Click Connection Details.
- In the Title box enter, or modify, the name of the Dimensions CM repository.
- In the Server box enter, or modify, the network name of the Dimensions CM server, for example:
dm-server.example.com - In the Dimensions CM base database name box enter, or modify, the database connection, for example:
CM_TYPICAL@DIM14These two values, separated by the @ symbol, are the same information that you enter in the DB name and DB connection boxes when you log into a Dimensions CM client. - For SCM Credentials, select or deselect the option Always use the following credentials. For details about using this option see below.
- Enter a Dimensions CM account username and password.
- Click Save.
Select Credentials to Access Dimensions CM Repositories
When Pulse accesses a Dimensions CM repository it presents a set of credentials. The credentials used for each repository depend on how you set the option Always use the following credentials in the repository connection:
- Selected: the CM account that you specify (see above) is used to connect to the Dimensions CM repository, which allows connections and caches to be pooled across users. Audit trail and user access control is the same as for the CM user. This option uses less disk space and fewer system resources.
- Unselected: the credentials of the user currently logged in Pulse are used to connect to the Dimensions CM repository. Audit trail and user access control is the same as for the Pulse user. The CM account that you specified is used for non-interactive connections to that repository when a logged in Pulse user is not available. This option provides better audit trail and access control.
Set Repository Defaults
Administrators can set repository defaults, such as integrations with Dimensions CM requests.
- On the top navigation click Administration.
- Select Repositories.
- Select a CM repository.
- Select Defaults.
- In the Reviewer Role in CM section enter a Dimensions CM role. Users that hold this role can be selected as reviewers in Pulse. If you do not specify a role the default REVIEWER is used.
- In the Integrating with CM Requests section do the following:
- In the In Review state name in CM box enter a comma separated list of CM request states that can add reviewers to associated Pulse reviews. Pulse listens for Action Request notifications from Dimensions CM. When a request enters one of these named states in CM, its Reviewer role assignment is copied to Pulse, and its review rules are executed.
- In the Rework state name in CM box enter the CM state to which requests are actioned when any associated Pulse review is sent for rework.
- In the Approved state name in CM box enter the CM state to which requests are actioned when any associated Pulse review is sent for rework or marked as approved.
- Actioning a request to In Review causes the review rules to run and will typically change the review's state to In Review.
- These integrations are optional. Leave blank to disable an integration.
- Leave all boxes blank unless your CM request lifecycle includes an In Review state.
- If you do not want to automatically copy role assignments to Pulse, or push states from Pulse, do not use this integration. Users can make changes manually in Pulse and Dimensions CM without this integration.
- Leave the boxes blank to disable the integration between Pulse reviews and Dimensions CM requests.
NOTE - Click Save.
Specify Expert Chain Capabilities
If you are an administrator you can mandate particular capabilities for each machine that runs an expert chain, for example:
- A specific Tomcat server (if you have multiple Tomcats running on the same machine).
- A specific application, for example: Java
When the expert chain runs, its requirements and all the machine capabilities and are matched. Only machines that match the requirements can run the chain. For example, if a chain requires Java, only machines where Java is installed can run the chain.
Specify Machine Capabilities
- On each machine where you want to specify capabilities, open this Pulse configuration file:
${dataDir}/conf/capabilities.properties - Enter a keyword for each capability, one per line, for example, Java.
- Save the file.
Add a Machine Requirement to an Expert Chain
- Select the stream containing the expert chain that you want to configure.
- On the sidebar select Expert Chains.
- Select the chain.
- Click Edit.
- Select the When to Run tab.
- In the Required capabilities field enter the machine capabilities (one per line) required by this expert chain, for example, Java.
These capabilities must match the keywords in the Pulse capabilities configuration file on each machine. Leave blank to run this expert chain on any machine. - Click Save.
Clear Caches
If you have made a configuration change and it is not visible, try clearing the relevant cache.
- On the top navigation click Administration.
- On the sidebar select Caches.
- Click Clear to empty a cache.
- To clear all caches click Clear All.
Other Administration Information
For information about the following Pulse administration topics see the Dimensions CM Administrator's Guide:
- Location of Serena common tools and Serena Pulse data folders.
- Customizing rule scripts.
- Setting the JDBC URL.
Use the Markdown Syntax
About the Markdown Syntax
Markdown is a syntax used to format information in plain text. You can use Markdown in any external text editor and copy the contents to Pulse, retaining a consistent look for all comments. The formatting is created with special sequences of punctuation characters in plain text.
Character Formatting
*This is italicized*, and so is _this_ |
This is italicized, and so is this |
**This is bold**, and so is __this__ |
This is bold, and so is this |
***Italics and bold*** together, as is ___this___ |
Italics and bold together, as is this |
Inline Code and Code Blocks
`Back-quote character` (also known as backtick |
Back-quote character (also known as backtick or grave) is used for inline code |
Use 4 space indent for code blocks. |
Use four space indent for code blocks. Some code line 1 Back to normal text again. |
Line Breaks and Paragraphs
Normally a single newline |
Normally a single new line is ignored.
|
End a line with two spaces |
End a line with two spaces to cause an explicit line break. |
Separate paragraphs. |
Separate paragraphs. With a blank line. |
Add a > to the beginning of a line to create |
Add a > to the beginning of a line to create a block quotation
Multiple quoted lines will wrap together. |
Simple Lists
- Use a minus sign for a bullet |
|
1. Numbered lists can use |
|
Links
Basic link to http://example.com. |
Basic link to http://example.com.
|
Inline link to [An Example Web Site](http://example.com/). |
Inline link to An Example Web Site. Numbered reference link to An Example Web Site. Named reference link to An Example Web Site. |
Headers and Rules
Header 1 |
Header 1 |
Header 2 |
Header 2 |
A horizontal rule is three or more hyphens, |
A horizontal rule is three or more hyphens, asterisks, or underscores
on the same line with no other characters.
|
Configure Experts
About Configuring Experts
Pulse includes bundled and built-in experts:
- A built-in expert can only be upgraded or replaced when you update Pulse. It is core to the product and is not expected to change without changes to Pulse.
- A bundled expert is a standard expert that is shipped with Pulse. You can overwrite it as long as the newer version is backwards compatible with your version of Pulse.
- Additional and upgraded experts will be made available by Serena Software for download from the Serena Central community web site.
- You can write your own expert implementations if you have site-specific requirements or in-house utilities that you want to integrate with Pulse.
Except where specified all experts are either bundled or built-in.
Each expert section contains some, or all, of the following information:
- Overview: what the expert does and why you would use it.
- Prerequisites: external tools that the expert depends on.
- Configure: global server configuration files that must be set up, the fields
that you enter when configuring an expert, and whether the expert needs to be in a chain that uses a workspace.
A workspace is a directory that is allocated to a chain when it runs. The workspace is populated with the stream content (its files), so that the experts in the chain can analyze the stream content and report findings back to Pulse. Workspaces are limited and a chain may be delayed until one is allocated. Workspace directories are located in the Pulse data directory.
The notation ${dataDir} refers to the Pulse data
directory on the Pulse server, for example, C:\ProgramData\Serena\Pulse or
/opt/serena/dimensions/cm/pulse_data.
Changeset Summary Expert
The Changeset Summary expert is a built-in expert that counts the number of files added, deleted, and modified in each changeset. To track of the number of changes, which indicates the level of code churn, you can configure this expert to run on every changeset.
This expert has no prerequisites or configuration and does not require a workspace because it uses the changeset information.
Checkstyle Expert
Overview
The Checkstyle expert is a bundled expert that uses the Checkstyle development tool to check that Java code adheres to a defined coding standard.
Use Checkstyle to help you comply with Java coding standards by automating code checking. Checkstyle is highly configurable and can support most coding standards, for more information see: http://checkstyle.sourceforge.net
This expert has no prerequisites (the Checkstyle 5.7 libraries are embedded in the expert so there are no external tools to install).
Configure
Create Server Configuration File
To customize the Checkstyle rules to be checked by this expert, create an XML configuration file in
${dataDir}/conf/experts/com.serena.starlight/checkstyle/ on the Pulse server.
The default filename is config.xml.
The Checkstyle expert searches for a configuration file in the following sequence:
- If the field Configuration File Name specifies a filename, looks for that file in
${dataDir}/conf/experts/com.serena.starlight/checkstyle/. - If the field Configuration File Name is empty, looks for
config.xmlin the same directory on the Pulse server. - If the field Configuration File Name is empty, and
config.xmldoes not exist, uses a built-in configuration based on Sun Coding Conventions.
Configure Expert Settings
When you add this expert to an expert chain in Pulse modify the following properties:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Step Name | Enter a name for this step in the expert chain. |
| Configuration location | Select one of the following options:
|
| Configuration File Name | Specify the path and filename of a configuration file that you created on the Pulse server. |
Checkstyle operates on source code files so add the Checkstyle expert to a chain that populates a workspace.
SonarQube Expert
Overview
The SonarQube expert is a bundled expert that runs static analysis against source code in a repository and reports findings and metrics. You can use it to analyze your source code on every changeset, or on a regular schedule, and optionally record the defects and metrics in your SonarQube server.
Prerequisites
The SonarQube expert requires SonarQube Runner, a command line application, to be installed and configured on the Pulse server. A SonarQube server must be installed on your network (not necessarily on the Pulse server) for this expert to connect to. For details see the SonarQube web site.
SonarQube expert uses the Web Service Java Client to make REST requests to a SonarQube server and has been tested with SonarQube server version 5.1.2 (previous versions of Pulse supported version 5.0).
The server configuration file ${dataDir}/conf/experts/com.serena.starlight/sonarqube/sonarqube-pulse-expert.properties
must be present and set up correctly before you can use SonarQube expert.
Configure
Create Server Configuration File
The SonarQube expert properties file is mandatory and is located in: ${dataDir}/conf/experts/com.serena.starlight/sonarqube/sonarqube-pulse-expert.properties
| Property Name | Description | Required | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| sonar.host.url | Specifies the SonarQube Server URL. | Yes | http://localhost:9000 |
| pulse.sonar.agent.path | Specifies the full path to the SonarQube Runner application. | Yes | C:\\sonarrunner\\bin\\sonar-runner.bat |
| sonar.jdbc.url | Specifies the JDBC connection URL for the SonarQube database. | No | jdbc:h2:tcp://localhost:9092/sonar |
| sonar.jdbc.username | Specifies the database user for the JDBC connection. | No | sonar |
| sonar.jdbc.password | Specifies the database password for the JDBC connection. | No | sonar |
| pulse.results.delay | When SonarQube analyzes code that produces a large number of findings (2000) a short delay is needed before the results can be fetched. This delay is normally only required on the first run. On subsequent runs only the delta needs to be updated. Default: 30 seconds | No | 30 |
If you do not specify an optional property SonarQube Runner uses the default value specified in ${SONAR_RUNNER_HOME}/conf/sonar-runner.properties.
You can configure additional supported parameters in ${SONAR_RUNNER_HOME}/conf/sonar-runner.properties.
Configure Expert Settings
When you add this expert to an expert chain in Pulse modify the following properties:
| Field Name | Description | Required | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Step Name | Enter a name for this step in the expert chain. | Yes | SonarQube |
| Username | Specifies the username for the web server connection. | No | admin |
| Password | Specifies the password for the web server connection. | No | admin |
| Analysis mode | Select an analysis mode:
|
Yes | analysis |
| Project name | Specifies the name of the SonarQube project that will be displayed in the web browser. Typically this is the value defined for <name> in Maven. | Yes | my_project |
| Project key | Specifies the unique SonarQube project key. Typically this is the value defined for<groupId>:<artifactId> in Maven. | Yes | example-key or com.example:project1 |
| Project version | Specifies the SonarQube project version. Typically this is the value defined for<version> in Maven. | Yes | 1.0 |
| Source folder | Specifies the relative stream folder in the workspace to run the analysis against. | Yes | src/main/java |
The properties Username and Password are optional and are only required in specific security situations, see the SonarQube web site for details.
The SonarQube Runner operates on source code files so add the SonarQube expert to a chain that populates a workspace.
Jenkins Expert
Overview
The Jenkins expert is a bundled expert that can invoke a Jenkins job on a remote Jenkins server. For example, use it to run a continuous integration build against each changeset as it is delivered and report the build time.
Prerequisites
The Jenkins server must be installed on your network, but not necessarily on the Pulse server, for this expert to connect to. See the Jenkins web site for more information about installing.
You must define a job on your Jenkins server that the expert will invoke.
Optionally add build parameters to the job so that information about the Dimensions CM stream and changeset are available in your build. Alternatively, allow the Jenkins expert to make any configuration change to the Jenkins job automatically (no manual changes to your Jenkins job are needed).
If you add the build parameters manually select the option This build is parameterized in your Jenkins job configuration page and add each build parameter as a String Parameter. The values of Default Value and Description in Jenkins are not important.
| Parameter Name | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| cmkey | An opaque value that uniquely identifies the build run to the Jenkins expert. Although shown here as Required, the Jenkins expert can automatically add this parameter to your Jenkins job and no manual job configuration is needed. |
Yes |
| repo | An opaque value that is different for each SCM repository. | No |
| stream | The name of the stream or project to which there was a delivery. | No |
| version | The stream or project version that the delivery created. | No |
| changeset | The repository (forest) version of the changeset for the delivery. | No |
Configure
When you add this expert to an expert chain in Pulse modify the following properties:
| Field Name | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| Step Name | Enter a name for this step in the expert chain. | Yes |
| Jenkins Job Location | Specifies the URL for the Jenkins job (the location of the continuous integration server, including the job name). | Yes |
| Username | Specifies a Jenkins username. May be required if you are using Jenkins authentication. | No |
| Password | Specifies a Jenkins password or API token of the Jenkins user. May be required if you are using Jenkins authentication. | No |
| Automatically add build parameters to Jenkins Job | Automatically reconfigure the Jenkins job to add the mandatory build parameter cmkey. You can also add parameters manually (see above) if you prefer that the Jenkins expert does not touch your job. | No |
| Record Jenkins Job build result | Specifies whether the Jenkins expert should monitor the job and record its state it completes. | No |
| Check Jenkins Job status every (seconds) | If Record Jenkins Job build result is selected, specifies how often the Jenkins expert checks if the job has completed. | No |
- Select your name at the top-right of the Jenkins page.
- From the Actions menu select Configure.
- Click Show API Token.
If your Jenkins job requires a build authentication token before it can be triggered (see this
Jenkins wiki page for details)
add the token to the end of the Jenkins URL, for example: http://hostname:port/jenkins/job/MyProject/?token=buildtoken
The Jenkins expert uses the parameters after the question mark in the build request URLs that are sent to the Jenkins server.
Jenkins manages its own workspaces so you can add the Jenkins expert to a chain that does not populate a workspace.
PMD Expert
Overview
The PMD expert is a bundled expert that scans Java source code (and other languages) and looks for potential problems such as bugs, dead code, suboptimal code, overcomplicated expressions, and duplicate code. You can use it to find common programming flaws during your code review process. PMD is configurable and can find many different issues, for more information see the PMD web site.
This expert has no prerequisites (the PMD 5.3.7 libraries are embedded in the expert so there are no external tools to install).
Configure
When you add this expert to an expert chain in Pulse modify the following configuration fields:
| Field Name | Description | Required | Example | PMD command line option | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step Name | Enter a name for this step in the expert chain. | Yes | PMD | ||
| Source folder | Enter the relative stream folder to run the analysis against. | Yes | src/main/java | -dir | Should be a relative path. |
| Rulesets location | Select a ruleset location:
|
Yes | |||
| Rulesets | Enter a comma separated list of rulesets names to use. | Yes | rulesets/internal/all-java.xml | -rulesets | See the full list of possible rulesets: http://pmd.sourceforge.net/pmd-5.2.3/. You can also use a custom ruleset. |
| Project classpath | Specify the classpath for libraries used by the source code. | No | commons-collections.jar;derby.jar | -auxclasspath | |
| Source encoding | Specify the source code encoding. | No | UTF-8 | -encoding | |
| Source language | Specify the source code language. | No | Java | -language | |
| Language version | Specify the language version. | No | 1.7 | -version | |
| Show suppressed | Show suppressed findings. | No | false | -showsuppressed | |
| Suppress marker | Specify the suppress marker. | No | NOPMDNEWMARKER | -suppressmarker |
The PMD command line option column shows how each PMD expert configuration field maps to the PMD command line tool. For details see: http://pmd.sourceforge.net/pmd-5.2.3/usage/running.html.
PMD operates on source code files so add the PMD expert to a chain that populates a workspace.
Kiuwan Expert
Overview
The Kiuwan expert is a bundled expert that integrates with Kiuwan Software Analytics in the Cloud, an online code quality and security service. If you are signed up to the Kiuwan service use this expert to:
- Track the quality and security of your changesets.
- Make that information visible in Pulse reviews and reports.
Prerequisites
You must have an active account (username and password) for the Kiuwan service, have logged into the service, and configured an application name for your stream.
You must install the Kiuwan Local Analyzer on the Pulse server.
Configure
Create Server Configuration File
The Kiuwan expert's server configuration file is mandatory and is located in: ${dataDir}/conf/experts/com.serena.starlight/kiuwan/kiuwan-pulse-expert.properties
| Property Name | Description | Required | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| kiuwan.agent.command | Specifies the full path to the Kiuwan Local Analyzer's agent launcher (agent.cmd or agent.sh not kiuwan.cmd or kiuwan.sh). | Yes | C:\\KiuwanLocalAnalyzer\\agent.cmd |
| kiuwan.poll.interval | Specifies how often to check whether an analysis has completed (seconds). | Yes | 180 |
| kiuwanUsername | Specifies the username (email) used to log into the Kiuwan service. | No | cibuild@example.com |
| kiuwanPassword | Specifies the password to log into the Kiuwan service. | No | I@m!S3cR3t |
| kiuwanAnalysisApplication | Specifies the application name that has been configured in the Kiuwan account. | No | Qlarius |
- You can specify the properties kiuwanUsername and kiuwanPassword when you add the Kiuwan expert to an expert chain. However, if you always use the same account it is more convenient to specify them in the server configuration file.
- Normally the property kiuwanAnalysisApplication will vary based on the stream. However, if you always use the same application name you can specify it globally in the server configuration file.
Configure Expert Settings
When you add this expert to an expert chain in Pulse modify the following fields:
| Field Name | Description | Required | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Step Name | Enter a name for this step in the expert chain. | Yes | Kiuwan |
| Username | Specifies a username for the Kiuwan account. | No | cibuild@example.com |
| Password | Specifies the password for the Kiuwan account. | No | I@m!S3cR3t |
| Application | Specifies the application name to register analysis results against in your Kiuwan account. | No | Qlarius |
The properties Username, Password and Application are only optional if they have been configured in the server configuration file.
The Kiuwan Local Analyzer operates on source code files so add the Kiuwan expert to a chain that populates a workspace.
SDA Deployment Expert
Overview
The SDA Deployment expert is a bundled expert that allows you to integrate Pulse with Serena Deployment Automation (SDA) and to publish and deploy artefacts from a Dimensions CM stream.
You can use the SDA Deployment expert to automate the path to production for your application. For example, the expert can support continuous delivery by:
- Publishing files from a stream to an SDA server as a new component version.
- Adding an SDA status to a new published version.
- Deploying the new published version.
Prerequisites
The SDA server must be installed on your network, but not necessarily on the Pulse server, where this expert can connect to it. SDA Deployment expert has been tested with SDA server version 6.1.1.
You will need a working application process configured in your SDA server for the SDA Deployment expert to invoke.
Configure
Create Server Configuration File
The following SDA Deployment expert properties file is usually required:
${dataDir}/conf/experts/com.serena.starlight/sdadeploy/sda-pulse-expert.properties
The property below identifies the location of the SDA server, if the default value shown is correct you do not need to edit it:
| Property Name | Description | Required | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| sdaServerUrl | URL to the SDA server web application | Yes | http://localhost:8080/serena_ra |
Configure Expert Settings
When you add this expert to an expert chain in Pulse modify the following configuration fields:
| Field Name | Description | Example | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| Step Name | Enter a name for this step in the expert chain. | SDA Delpoyment | Yes |
| Username | Enter the username of an SDA server administrator. | admin | Yes |
| Password | Enter the password of the SDA server administrator. | admin | Yes |
| Component Name | Specify the name of the SDA component that will be published. | my_component_1.5 | Yes |
| Version | A new version of an SDA component is created each time this expert runs. Use this option to specify the format of the version name and make it easier to identify its source. You can include the following variables by using the syntax '$(<variable name>)' in the value. CHANGESET_ID EXPERT_RUN_ID PRODUCT_NAME STREAM_NAME STREAM_VERSION |
'VERSION_NAME-$(CHANGESET_ID)' | Yes |
| Artifact directory | Specify the relative path in the stream where assets are located. | target\ | Yes |
| Include | To only publish specific files, enter one or more Ant patterns (one per line). To publish all files leave this field blank. | *.war *.jar |
No |
| Exclude | To exclude specific paths from being published, enter one or more Ant patterns (one per line). To publish all files leave this field blank. | *.java *.html *.xml |
No |
| Add Status | Select this option to display the field Status Name. | No | |
| Status Name | (Visible if Add Status is selected) Specifies the SDA status to move the new component version to. | STATUS_SUCCESS | Yes (if Add Status is selected) |
| Deploy | Select this option to display fields that specify how the new component version will be deployed. | No | |
| Application Name | Specify an SDA application (contains a component to be deployed). | my_application | Yes (if Deploy is selected) |
| Application Process Name | Specify the SDA application process to be executed. | my_deploy_app_process | Yes (if Deploy is selected) |
| Environment Name | Specify the SDA environment to deploy to. | my-environment | Yes (if Deploy is selected) |
| Deploy Properties | Specify deploy properties that will be used to run the SDA application process. Enter one pattern per line in this format: <property_name>=<prop_value> |
set_up_db=true use_logging_level=trace |
No |
SDA normally operates on binary files so add the SDA Deployment expert to a chain that populates a workspace with built artefacts.
SDA Generic Process Expert
Overview
The SDA Generic Process expert is a bundled expert that allows you to integrate Pulse with Serena Deployment Automation (SDA) and run a SDA global process on a specific SDA resource. For example, you can use this expert to run a regular, repeated process when updated artefacts are delivered.
Prerequisites
The SDA server must be installed on your network, but not necessarily on the Pulse server, where this expert can connect to it. SDA Generic Process expert has been tested with SDA server version 6.1.1.
You will need a working global process configured in your SDA server for the SDA Generic Process expert to invoke.
Configure
Create Server Configuration File
The following SDA Generic Process expert properties file is usually required:
${dataDir}/conf/experts/com.serena.starlight/sdaprocessexecutor/sda-pulse-expert.properties
The property below identifies the location of the SDA server, if the default value shown is correct you do not need to edit it:
| Property Name | Description | Required | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| sdaServerUrl | URL to the SDA server web application | Yes | http://localhost:8080/serena_ra |
Configure Expert Settings
When you add this expert to an expert chain in Pulse modify the following fields:
| Field Name | Description | Example | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| Step Name | Enter a name for this step in the expert chain. | SDA Generic Process | Yes |
| Username | Enter the username of an SDA server administrator. | admin | Yes |
| Password | Enter the password of the SDA server administrator. | admin | Yes |
| Generic Process Name | Specify the name of the SDA global process to be run on the SDA server. | setup_net_process | Yes |
| Resource Name | Specify the name of the SDA resource on which the global process will be run. | machine_without_net_resource | Yes |
| Process Properties | Specify properties that will be used to run the SDA global process. Enter one pattern per line in this format: <property_name>=<property_value> |
set_up_db=true use_logging_level=trace |
No |
SDA normally operates on binary files so add the SDA Generic Process expert to a chain that populates a workspace with built artefacts.
Dependency Vulnerabilities Expert
Overview
The Dependency Vulnerabilities expert is a bundled expert that integrates the Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP) dependency-check tool that can scan Java, .NET, and Python applications and their dependent libraries.
This expert identifies vulnerable dependencies in the analyzed stream and displays the findings in the Experts section of a Pulse Review page. One finding per vulnerability is displayed and there can be multiple vulnerabilities for each dependency. Each finding contains the ID of the vulnerability and the name of the dependency where it was found. A report file can be viewed from the Review page.
Prerequisites
There is no external software to install (the dependency-check 1.3.6 library is embedded in the Dependency Vulnerabilities expert). However, the expert relies on data from the National Vulnerabilities Database (NVD) web site to find vulnerabilities and requires access to the internet to download and update data.
On the first run the expert creates:
- The folder
${dataDir}/conf/experts/com.serena.starlight/dependencyvulnerabilities/data/ - The file
cve.2.9.h2.dbthat is updated from the Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) data . Each run automatically updates the CVE data if autoupdate in the properties file is set to true.
Configure
Create Server Configuration File
The properties file is optionally located in ${dataDir}/conf/experts/com.serena.starlight/dependencyvulnerabilities/dependencycheck-pulse-expert.properties.
It contains configuration properties for both the Dependency Vulnerabilities expert and its embedded dependency-check library.
You only need to create this file if you need to override one of the default values.
| Property Name | Description | Example Value | Default Value | Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pulseWarningCvssThreshold | Vulnerabilities with a CVSS score less than the specified value are treated as a WARNING. | 3.0 | 4.0 | No |
| pulseErrorCvssThreshold | Vulnerabilities with a CVSS score less than the specified value are treated as an ERROR. The value must be bigger than that specified for pulseWarningCvssThreshold. | 9.0 | 7.0 | Yes |
| pulseAutoUpdate | Automatically updates the CVE data. The possible values are:
|
ALWAYS |
Configure Expert Settings
When you add this expert to an expert chain in Pulse modify the following fields:
| Field Name | Description | Example Value | Default Value | Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step Name | Enter a name for this step in the expert chain. | Dependency Vulnerabilities | Dependency Vulnerabilities | Yes |
| Application name | Enter the application name to be displayed in the report file. | My-App | Yes | |
| Include patterns | To only include specific paths, enter one or more Ant patterns (one per line). To include all paths leave blank. | *.war **/*.jar |
**/* | No |
| Exclude patterns | To exclude specific paths, enter one or more Ant patterns (one per line). To include all paths leave blank. | target/*.class | No | |
| Suppression file | Enter the relative path in the stream to the suppression file. | conf/suppression.xml | No | |
| CVE Suppression List | Enter a comma-separated list of CVE IDs to suppress. | CVE-2008-0732,CVE-2011-5034 | No | |
| Enable Archive analyzer | Scans these files types: ZIP, EAR, WAR, JAR, SAR, APK, NUPKG, TAR, GZ, TGZ | Yes | No | |
| Enable Jar analyzer | Scans these files types: JAR, WAR | Yes | No | |
| Enable Assembly analyzer | Scans these files types: EXE, DLL | Yes | No | |
| Enable Nuspec analyzer | Scans the NUSPEC file type. | Yes | No | |
| Enable Python package analyzer | Scans these files types: py, zip, PKG-INFO, METADATA | Yes | No | |
| Enable Python distribution analyzer | Scans these files types: whl, egg, zip | Yes | No | |
| Enable CMaker analyzer | Scans these files types: CMakeLists.txt, *.cmake | No | ||
| Enable NodeJS analyzer | Scans this file type: package.json | No | ||
| Enable OpenSSL analyzer | Scans this file type: opensslv.h | No | ||
| Enable Ruby analyzer | Scans these files types: rakefile, *.gemspec | No | ||
| Enable Composer Lock analyzer | Scans this file type: composer.lock | No | ||
| Enable Autoconf analyzer | Scans these files types: configure, configure.in, configure.ac | No | ||
| Enable Central analyzer | Checks for Maven GAV (Group/Artifact/Version) information in the scanned area. | Yes | No | |
| Enable Nexus analyzer | Checks for Maven GAV (Group/Artifact/Version) information in the scanned area. | Yes | No | |
| Unstable threshold | If there are vulnerabilities with a CVSS score higher than the value you specify, the expert result is UNSTABLE. If no value is set the result is SUCCESS. | 7.0 | No | |
| Failure threshold | If there are vulnerabilities with a CVSS score higher than the value you specify, the expert result is FAILURE. If no value is set the result is SUCCESS. | 9.0 | No | |
Automatically update CVE DB |
Select an update option for the CVE database:
|
For more information about analyzers see this web page.
The Dependency Vulnerabilities expert may report false-positive dependencies. For example, you consume a vulnerable library but you do not use the vulnerable functionality, or the vulnerability only applies in circumstances that does not apply to you. You can suppress any CVE by passing the suppression XML file with CVE suppressions (Suppression file property) or the CVE ID list (CVE suppression list property). For more information about suppression see this web page.
The dependency-check analyzers operates on binary files so add the Dependency Vulnerabilities expert to a chain that populates a workspace with built artefacts.
CM Build Expert
Overview
If your team uses Dimensions Build and you have existing build configurations, the bundled CM Build expert enables you to run the configurations in Pulse. Dimensions Build is a build management, execution, and monitoring tool that is part of Dimensions CM. For details see the Dimensions CM Build Tools User's Guide.
Prerequisites
A build configuration, created in Dimensions Build, for each stream that you are going to build.
Configure
When you add this expert to a chain configure it as follows:
- Enter a name for this step in the expert chain.
- Select a CM user account to be used to run the build:
- Service account: use the account and credentials of the user current logged into Pulse. This is the account that was used to populate the work area associated with the stream.
- Custom account: use a different CM user account. Specify the user name and password.
- Set Configure using command line to one of the following:
- Yes: enter a BLD command and specify a poll rate. For details of the BLD command see the Dimensions CM Command-Line Reference.
- No: configure CM Build using the fields described below.
| Field Name | Description | Required | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Build based on request(s) | Restrict the build to sources that are related to CM requests that you specify. Enter a comma separated list of requests. Leave blank if you do not want to restrict the build. | QLARIUS_CR_21,QLARIUS_CR_56 | |
| Area type | Select a Dimensions CM area type:
|
||
| Area name | Specify the area to be used for this build. Default: all areas associated with the build configuration or stage. | ||
| Stage | Specify the stage where the targets will be built. Only displayed if you select a Deployment area. |
DEV | |
| Build configuration name | Specify the build configuration, and version, that you want to build. If you do not specify a version, by default the latest is used. | Yes | ANT_JAVA_BUILD;6 |
| Build area user | Enter a Dimensions CM credential set that has access to the build area. Only displayed if you select a Work area. |
MY_CREDENTIAL_SET | |
| Populate the work area with all files | Select this option to populate the work area with all the files that are related to the build. Only displayed if you select a Work area. |
||
Check in built items
|
Select one of the following options:
|
||
| Target stream name | Specify the stream where the collected and built items will be delivered. Default: the same stream as the sources. Only displayed if you are checking in built items. |
QLARIUS:JAVA_BRANCHA_STR | |
| Relate built items to requests | Specify a comma separated list of requests to which new items created from the final build targets will be related. Only displayed if you are checking in built items related to custom requests. |
QLARIUS_CR_24,QLARIUS_CR_18 | |
| Build options | Select one of these options:
Only displayed if you select a Deployment area. |
||
| Target selection |
For details see the BLD command in the Dimensions CM Command-Line Reference. |
||
| Poll rate | Specify how often (in seconds) that the expert checks if the build has completed. | Yes | 50 |
CM Build manages its own workspaces so you can add it to a chain that does not populate a workspace.
HP Fortify SCA Expert
Overview
The HP Fortify SCA expert is a bundled expert that analyzes the source code of an application for security issues. Static Code Analyzer (SCA) identifies the root causes of software security vulnerabilities and delivers accurate, risk-ranked results with line-of-code remediation guidance.
Prerequisites
The HP Fortify SCA expert requires HP Fortify SCA (and any tools that it will use, such as Microsoft Visual Studio) to be installed and configured correctly for the user account that Tomcat will run as.
Configure
Create Server Configuration File
The HP Fortify SCA expert's server configuration file is mandatory and is located in: ${dataDir}/conf/experts/com.serena.starlight/hpfortify/hpfortify-pulse-expert.properties
| Property Name | Description | Required | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| sourceAnalyzerPath | Specifes the full path to HP Fortify SCA. | Yes | C:\\Program Files\\HP_Fortify\\HP_Fortify_SCA_and_Apps_4.30\\bin\\sourceanalyzer.exe |
| reportGeneratorExecutablePath | Specifes the full path to the HP Fortify SCA report generator. | Yes | C:\\ProgramFiles\\HP_Fortify\\HP_Fortify_SCA_and_Apps_4.30\\bin\\ReportGenerator.bat |
| visualStudioExecutablePath | Specifies the full path to Microsoft Visual Studio. | No | C:\\Program Files (x86)\\Microsoft Visual Studio 10.0\\Common7\\IDE\\devenv.exe |
Example server configuration file:
sourceAnalyzerPath=C:\\Program Files\\HP_Fortify\\HP_Fortify_SCA_and_Apps_4.30\\bin\\sourceanalyzer.exe reportGeneratorExecutablePath=C:\\ProgramFiles\\HP_Fortify\\HP_Fortify_SCA_and_Apps_4.30\\bin\\ReportGenerator.bat visualStudioExecutablePath=C:\\Program Files (x86)\\Microsoft Visual Studio 10.0\\Common7\\IDE\\devenv.exe
Configure Expert Settings
When you add this expert to a chain configure it as follows:
- Enter a name for this step in the expert chain.
- Select a custom translation option:
- Yes: use a custom translation string. Enter a string in Custom translation options but only include phase options and exclude '-b'.
- No: select translation options (see the table below).
- For Analysis phase optionally enter additional rulepack files or folders, one per line. You can specify an absolute path or one that is relative to the root of the stream. Use the sourceanalyzer Ant task rules attribute.
- To create a PDF of the report select Generate PDF report and enter the path of a report template. You can specify an absolute path or one that is relative to the root of the stream. If you do not specify a report template the default is used. Use the ReportGenerator utility's template option.
| Translator type | Option | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Java sources | Sources include pattern | Enter patterns for Java sources, for example: src/**/ *.java Default pattern: **/*.java |
Classpath |
Enter a Java class path. The format is the same as javac (colon or semi-colon separated list of paths). Use the sourceanalyzer Ant task classpath attribute. | |
| Resolution source path | Enter a path to a Java resolution sources folder. Sources are used for resolution not analysis. Use the sourceanalyzer Ant task sourcepath attribute. | |
Java version |
Specify the JDK version the Java code is written for. Use the sourceanalyzer Ant task source attribute. | |
| .NET sources | Solution file path | Enter the relative path to a solution file. |
| Other sources | Include pattern |
Enter an 'include' pattern for other sources, for example: **/ *.sql |
Script Expert
Overview
The Script expert is a bundled expert that enables you to specify one of the following:
- An operating system command.
- The path to a file, for example, a Windows batch file or UNIX shell script.
Configure
When you add this expert to a chain, configure it as follows:
- Enter a name for this step in the expert chain.
- From the Type of script list select one of the following:
- Use inline command and enter an operating system command in the Command line box.
- Use file path and enter the path in the File path box.
You can use the following environment variables:
- PULSE_STREAMTITLE: the name of the project or stream.
- PULSE_STREAMVERSIONID: the project or stream version.
- PULSE_SCMCONNECTIONURI: a unique identifier for the Dimensions CM database.
- PULSE_LOGINNAME: the user who made the delivery.
- PULSE_MESSAGE: the commit message for the delivery.
- PULSE_DIRECTORY: the location of the workspace containing the source code.
- CURRENT_DIR: same as PULSE_DIRECTORY (also set as the working directory of the script).
All the variables in the environment.properties file are available to the script as environment variables.
If the script exits with an exit code of 0, it is a SUCCESS. If the script exits with a non-zero exit code, it is a FAILURE.
WhiteSource Expert
Overview
The WhiteSource expert is a bundled expert that identifies all the open source components and dependencies in your build, reports any known security vulnerabilities, and lists their licenses.
Prerequisites
- An active organization (and API token) for the WhiteSource SaaS service.
- Access to the WhiteSource administrative site.
- A product and project to report results to.
- The project token.
Configure
Create Server Configuration File
The WhiteSource expert's server configuration file is located in: ${dataDir}\conf\experts\com.serena.starlight\whitesource\whitesource-pulse-expert.properties
| Property Name | Description | Required | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| whitesourceServerUrl | Specifies the URL to the WhiteSource server. Only change this URL if you are using the on-premise version of WhiteSource. | No | whitesourceServerUrl=https://saas.whitesourcesoftware.com |
Example server configuration file:
whitesourceServerUrl=https://saas.whitesourcesoftware.com
Configure Expert Settings
When you add this expert to an expert chain in Pulse, specify the following fields:
| Field Name | Description | Example Value | Default Value | Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step Name | The name of this expert step. | WhiteSource |
WhiteSource | Yes |
| Api key | The API key of a product registered in WhiteSource (also known as organization token). Copy the value from WhiteSource. | Yes | ||
| Product token | The product token generated when registered in WhiteSource. Copy the value from WhiteSource. | No | ||
| Project token | The project token generated when the product was registered in WhiteSource. Copy the value from WhiteSource. | Yes | ||
| Include pattern | Use Ant patterns to include specific resources. Separate each pattern with a space. | **/*.jar | ||
| Exclude pattern | Use Ant patterns to exclude specific resources. Separate each pattern with a space. | **/*sources.jar **/*javadoc.jar | ||
| Poll delay | Specify how often, in seconds, the expert polls the WhiteSource database. | 120 | 30 | |
| Update Inventory | Select this option to update the WhiteSource project dashboard with new information that was found. If not selected, the information is only reported in Pulse. |
Troubleshoot
Administration Issues
Database not Accessible
If Pulse fails to start because it cannot connect to its database, a detailed exception message is displayed instead of the login page. A common reason is a missing or inaccessible database at application start up time. The logs in the Pulse data directory on the server contain more information. For information about configuring the JDBC URL, see the Pulse chapters in the Dimensions CM Administrator's Guide.
Reviews not Created Automatically
Reviews are not created automatically when deliveries are made to CM:
- If your Dimensions CM server is correctly configured to emit ALF events when a delivery is made, check that your repository connection has been setup properly and that Pulse can connect to it.
- In the stream's settings check that:
- The delivery filter is not set to exclude the changeset.
- Create/Attach to a Review is selected.
- If a delivery references a Dimensions CM request, or has a review label in the format [Q100] in the delivery message, the changeset may be associated with an existing review at the Draft or Rework state and will not create a new review.
User Avatar Images not Displayed
Try the following:
- Check that the avatar server is configured properly.
- Go to Administration | Caches and clear the avatar images cache.
- Clear your local browser cache.
Expert Chains do Not Start
If expert chains do not start when deliveries are made to CM check:
- The stream is configured to automatically run expert chains.
- The chain is configured to run on a schedule rather than every delivery.
- The Pulse server logs described in the Dimensions CM Administrator's Guide.
Expert Chain Results Not Displayed
If expert chains run successfully but results are not displayed, check that the parameters in Jenkins are configured correctly. Builds will run in Jenkins even if parameters are not configured correctly, but the results will not be sent to Pulse. You can also view expert chain logs.
For more information about configuring Jenkins see the Dimensions CM Build Tool User's Guide.
Other Issues
Reviewers Not as Expected
If the reviewers assigned to a new review are not as expected:
- Check that the design parts that own the files being reviewed are correct.
- Check who holds the Reviewer role on those design parts.
- A Pulse administrator can configure the Reviewer role for each repository.
- Pulse assigns reviewers differently to the way that roles are assigned to CM requests:
- Pulse takes a union of the users holding the role on the items' owning design parts.
- CM requests take the role assignments from a common ancestor design part in the design part hierarchy.
If item content is not displayed correctly in reviews, in the Dimensions CM administration console check that:
- The item's data format is set correctly.
- The data format has an appropriate MIME type. Items that have a data format with a MIME type beginning text/ are displayed as inline text, MIME types beginning with image/ are displayed as images.
Requests are Actioned but Pulse Reviews do Not Change State
If CM requests are actioned but the corresponding Pulse reviews do not change state, try the following:
- On the top navigation click Administration.
- Select Repositories.
- Select the review's repository and click Defaults.
- In the Reviewer role name in CM field see what CM role that has been specified. Users that hold this role can be selected as reviewers in Pulse.
- If the CM request does not have a user that holds this CM role, no changes are made in Pulse.
- If the CM request does have a user hold this CM role, the role assignment should have been copied to the review. However, the review rule script for the stream also determines if the review changes its state.
Check the ALF event configurations and Pulse server logs, see the Dimensions CM Administrator's Guide for details.
Pulse Reviews Change State but Requests are Not Actioned
If Pulse reviews change state but the corresponding CM requests are not actioned, try the following:
- On the top navigation click Administration.
- Select Repositories.
- Select the review's repository and click Defaults.
- In the Approved state name in CM and Rework state name in CM boxes check the state names are correct.
- Click Cancel.
- On the sidebar click Connection Details.
- In the Credentials section check that the specified user can log into Dimensions CM and that the user account has privileges in Dimensions CM to action requests to the necessary states.
- If a request in Dimensions CM requires mandatory attributes, enter them manually. Pulse cannot automatically populate the attributes unless the credentials on the repository are for an account that has privileges in Dimensions CM to bypass this requirement.
- Delegate any role assignments on requests in Dimensions CM that are required before the request can be actioned to the next state. Pulse does not change the role assignments on requests in Dimensions CM, even for the Reviewer role of the repository.
- Only reviews that change their state from In Review to Rework, or from In Review to Approved or Completed, cause their corresponding CM requests to be actioned. If a review is associated with multiple requests, all the requests are actioned. If a request is associated with multiple reviews, the request is actioned more than once.
- Check the Pulse server logs at the DEBUG level, see the Dimensions CM Administrator's Guide for details.
Unexpected Formatting in Review Comments
- Pulse uses Markdown syntax for formatting user comments. If you are expecting a new line in your comment, try ending the previous line with two spaces or using an extra blank line.
-
For security reasons the following are removed:
- Links or images that do not point to an URL of the type http:// or https://
- Unsafe or unbalanced HTML tags
PMD Expert
If the compilation unit (*.java file):
- Is not syntactically correct PMD does not report any findings therefore sources must be compiled successfully.
- Is very large, for example 10,000 lines, and there are multiple bugs PMD may take a long time to complete.
SonarQube Expert
If you have problems with SonarQube Runner see the web site.
If you receive the state Aborted check that:
- The expert property file is in:
${dataDir}/conf/experts/com.serena.starlight/sonarqube/sonarqube-pulse-expert.properties - All required properties are specified in the property file.
- The SonarQube server and database are up and running.
- The connection details to the SonarQube server and SonarQube database are configured correct in the property file.
- The path to the SonarQube Runner command line tool is correct in the property file.
Check the Pulse log file.
SDA Experts
Check the following:
- The configuration is set up properly, for example, the correct SDA object names are specified.
- If the property file is not found or is not set up correctly, the wrong SDA server URL may be specified.
- The SDA server version is supported.
- The SDA agent or resource is online.
Dependency Vulnerabilities Expert
Check the following:
- If autoupdate in the properties file is set to false, CVE data is not updated and the expert will not report any findings.
- The OWASP Dependency Check tool does not always work correctly with analyzer options and you may have to disable them. To exclude specific paths use the Exclude patterns field.
Contact Serena Support
Serena provides technical support for all registered users of this product, including limited installation support for the first 30 days. If you need support after that time, contact Serena Support and follow the instructions. Language-specific technical support is available during local business hours. For all other hours, technical support is provided in English.