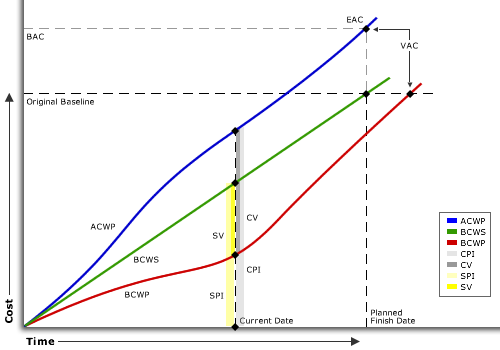
Earned value is a way to measure the performance of a task plan by using a series of calculations to compare actual and expected costs over the life of the project. All earned value calculations are measured by comparing the dates saved as part of the original baseline in the task plan to a specific date of your choosing, up to the current date.
The most important earned value calculations are actual cost of work performed (ACWP), budged cost of work scheduled (BCWS), and budgeted cost of work performed (BCWP); however, there are many other earned value calculations that are available for use in the task plan.
Earned values are best measured and tracked early in the task plan lifecycle. A project that is on track to being completed on time, under budget, and so on, will have healthy early indicators for earned value. Some earned value metrics such as cost performance index, the variance between its value 10-20% into the task plan is often close to its value at the point on which the task plan is completed.
Some important elements that can affect the quality of earned value data include: work breakdown structure, a good initial baseline for the task plan, and updated/current data added to the project for each task as its work progresses.
The following fields provides a description for all of the earned value fields that are available in a task plan:
| Earned Value | Description |
|---|---|
| ACWP |
Actual cost of work performed. The actual cost of all completed work, including resource costs, actual work, fixed costs, and so on, up to the current date. |
| BAC |
Budget at completion. The total planned cost to complete every scheduled task. This is sometimes called baseline cost. |
| BCWP |
Budgeted cost of work performed. The cumulative costs of planned work that has been actually completed, and then compared to the original estimates for that work. This is sometimes called earned value (EV). |
| BCWS |
Budgeted cost of work scheduled. The planned cost of total amount of work that has been scheduled. This is sometimes called planned value (PV). |
| CPI |
Cost performance index. The difference in value between the budgeted cost of work performed and the actual cost of work performed. The calculation for cost performance index is as follows: CPI = BCWP / ACWP. When the cost performance index is greater than 1, it is an indicator that the task plan is over budget. |
| CSI |
Cost schedule index. The difference in value between the cost performance index and schedule performance index. The calculation for cost schedule index is as follows: CSI = CPI x SPI. Cost schedule index should be as close to 1 as possible. When the cost schedule index is not one, it is an indicator that the task plan is behind schedule and over budget. The farther away from 1, the farther behind and/or over budget the task plan is. |
| CV |
Cost variance. The difference between planned costs of work performed and the actual costs of work performed. The calculation for cost variance is as follows: CV = BCWP - ACWP. When the cost variance is less than 1, it is an indicator that the task plan is over budget. |
| CV% |
Cost variance percentage. The percentage over or under budget, based on cost variance and the planned cost of work in the task plan. The calculation for cost variance percentage is as follows: CV% = CV / BCWP. When the cost variance percentage is greater than 1, it is an indicator that the task plan is under budget. |
| EAC |
Estimate at completion. The expected cost to complete all remaining work. The calculation for estimate at completion is as follows: EAC = ACWP + (BAC - BCWP). BAC - BCWP represents the planned costs of all uncompleted tasks. This is sometimes referred to as the estimate to complete (ETC). |
| Earned Value Method | Earned value method. This field is manually entered (and its value is not calculated). Use earned value method when there are tasks in a task plan that require physical percent complete. |
| Physical Percent (%) Complete | The percentage of work completed, measured independently of a task's duration. Use physical percent complete to manually override budgeted cost of work performed values when the process of completing a task can be measured independently of the task's duration. Sometimes used as an alternative to budgeted cost of work scheduled (BCWS). |
| SPI |
Schedule performance index. The difference in value between current progress and the expected progress. The calculation for schedule performance index is as follows: SPI = BCWP / BCWS. When the schedule performance index is less than 1, it is an indicator that the task plan is behind schedule. |
| SV |
Schedule variance. The difference in costs between current progress and expected progress. The calculation for schedule variance is as follows: SV = BCWP - BCWS. When the schedule variance is less than 0, it is an indicator that the task plan is behind schedule. |
| SV Percent (%) |
Schedule variance percent. A percentage that shows how well the schedule is doing in relation to the cost of scheduled work. The calculation for schedule variance percent is as follows: SV% = (SV / BCWS) * 100. When the schedule variance percentage is greater than 1, it is an indicator that the task plan is behind schedule. |
| TCPI |
To-complete performance index. A ratio of remaining work. The difference between the planned costs of all completed tasks to the to the planned costs of all remaining, uncompleted tasks. The calculation for to-complete performance index is as follows: TCPI = [BAC - BCWP] / [BAC - ACWP]. When the to-complete performance index is greater than 1, it is an indicator that close attention should be paid to all of the work that remains so that the task plan can stay within budget. |
| VAC |
Variance at completion. The difference between the the total planned cost to complete every scheduled task and the expected cost to complete all remaining work. The calculation for variance at completion is as follows: BAC - EAC. When the variance at completion is negative, it is an indicator that your task plan is over budget. |
The following diagram shows the relationship of earned value data points: